|
Name: para-Methylcyclopropylfentanyl (N-(4-methylphenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide)
Type: Synthetic opioid
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
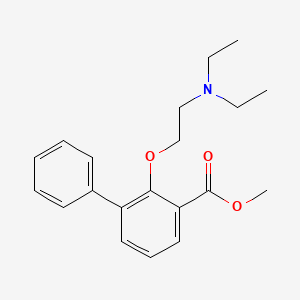
|
|
IV. History
Para-Methylcyclopropylfentanyl, a synthetic opioid, was first developed in the 2010s. It is an analog of fentanyl designed to increase potency and alter pharmacological properties. The compound's introduction reflects ongoing trends in synthetic opioid development. Its potency and association with overdose deaths have led to increased regulatory measures.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Para-Methylcyclopropylfentanyl is a synthetic opioid with a high potential for abuse. It is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States, reflecting its significant risk of addiction. Regulations in other countries also focus on controlling its use to prevent illegal distribution and misuse. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Para-methylcyclopropylfentanyl is a synthetic opioid known for its potent analgesic effects. It acts as a downer, causing significant sedation and respiratory depression. Short-term use can effectively manage pain, but long-term use may lead to addiction and tolerance. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use requires precise dosing and medical supervision. Recent research examines its potency and safety compared to other opioids.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
N/A
 |
|
VIII. Culture
2-(2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl)-N,N-diethylethan-1-amine is a research chemical with stimulant properties, classifying it as an upper. Short-term use may increase alertness and energy, while long-term effects are not well-documented. Overdose risks are moderate, potentially causing severe agitation and cardiovascular issues. Safe dosages are not well-established, with lower doses advised. Recent research focuses on its psychoactive potential and health risks. Physical effects may include increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and potential for severe agitation.
 |
