|
Name: (4-chlorophenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)isobutyramide Para-Fluoro furanyl fentanyl (N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)furan-2-carboxamide)
Type:
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
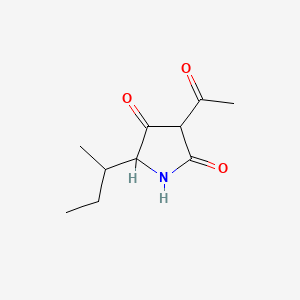
|
|
IV. History
This compound is a synthetic opioid developed in the 2010s. It is a derivative of fentanyl, known for its potency and effects. Its development reflects ongoing research into potent analgesics, though its use has been restricted due to safety concerns.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Para-Fluoro-Furanyl-Fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, is regulated as a controlled substance due to its high potential for abuse. Its status reflects efforts to manage opioid use and prevent misuse.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Para-Fluoro Furanyl Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid with potent analgesic effects. As a downer, it induces significant pain relief and sedation. Short-term effects include reduced pain and euphoria, while long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks involve severe respiratory depression and potential fatality. Safe dosing requires careful medical supervision. Recent research focuses on its efficacy and risks of misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
This fentanyl analog affects opioid receptors, resulting in intense euphoria and cognitive impairment. Immediate effects are significant mood enhancement and pain relief, while long-term use can lead to dependence, cognitive decline, and psychological distress. Effects are rapid and can last a few hours, with long-term abuse potentially causing severe mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Para-fluoro furanyl fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use provides strong analgesic effects, while long-term use can lead to dependence, tolerance, and severe health risks. Overdose risks are extremely high, causing severe respiratory depression and potential fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are not well-established, with use often limited to controlled medical settings. Recent research emphasizes its potency and potential for misuse. Physical effects include drowsiness, constricted pupils, and respiratory depression.
 |
