|
Name: 1-androstenedione (5-alpha-androst-1-en-3,17-dione)
Type: Androgenic steroid
AKA: N/A
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
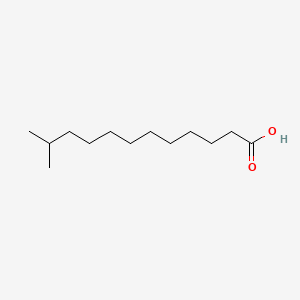
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
1 androstenedione was first isolated from the urine of pregnant mare urine (PMU) mice in 1965. This was the first time that a steroid was isolated from the urine of a pregnant mammal. However, the structure of 1 androstenedione was not reported until 1969. 1 androstenedione was found to be a metabolite of the steroid hormone, testosterone. 1 androstenedione is a precursor to testosterone, androstenedione and dihydrotestosterone.
The structure of 1 androstenedione was determined by Dr. Roger P. Daughaday, Jr., at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The structure of 1 androstenedione was determined to be:
1 androstenedione, the major urinary metabolite of testosterone, was first isolated from the urine of pregnant mare urine (PMU) mice in 1965. This was the first time that a steroid was isolated from the urine of a pregnant mammal. However

|
|
V. Legal Information
1-Androstenedione is an anabolic steroid used to enhance athletic performance. It is regulated under steroid laws in the U.S. and faces similar controls internationally to prevent misuse in sports and bodybuilding. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
1-Androstenedione is a steroid hormone used for muscle enhancement. It acts as an upper, promoting muscle growth. Short-term use can improve physical performance, but long-term use may cause hormonal imbalances and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe health complications. Safe use involves careful dosing and monitoring. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and associated health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
1-Androstenedione, an anabolic steroid, influences mood and aggression through androgen receptor interactions. Immediate effects include increased energy and improved mood. Long-term use can lead to mood swings, aggression, and cognitive impairments. Research highlights its impact on neurotransmitter systems and the psychological risks of long-term steroid use, including mood disorders and aggression.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
1-Androstenedione is a steroid hormone precursor, classifying it as a performance enhancer. It boosts muscle mass and strength in the short term. Long-term use can lead to cardiovascular issues, liver damage, and hormonal imbalances. Overdose risks include severe cardiovascular problems, liver toxicity, and reproductive health issues. Safe dosages are controlled and typically prescribed by medical professionals. Recent research highlights its potential to increase muscle mass but warns of cardiovascular and liver health risks. Physical effects include increased muscle mass, elevated heart rate, and potential mood changes.
 |
