|
Name: 2-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitro-phenyl) ethanamine (2C-N)
Type: Psychedelic phenethylamine
AKA: 2C-N
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
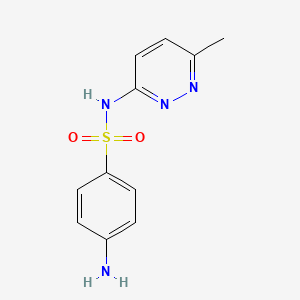
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
2C-N, a synthetic psychedelic, was first synthesized in the 1970s by Alexander Shulgin. It is a member of the 2C family, known for its psychoactive effects. The compound was studied for its potential as a therapeutic agent and for recreational use. 2C-N's appearance in the recreational drug market highlighted its psychoactive properties and led to regulatory actions aimed at controlling its availability and addressing safety concerns.

|
|
V. Legal Information
2C-N is a psychedelic compound with hallucinogenic effects. It is controlled in many regions due to its potential for abuse and impact on mental health. International regulation reflects concerns about its misuse. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
2C-N is a psychedelic phenethylamine first synthesized in the 1970s. It acts as an upper, causing altered perception and euphoria. Physical impacts include dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and elevated blood pressure. Short-term use can lead to intense sensory experiences and psychological effects, while long-term use may result in cognitive distortions. Overdose risks include severe psychological distress and cardiovascular issues. Safe use requires careful dosing to avoid adverse effects. Recent studies focus on its psychoactive properties and potential for therapeutic applications.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
2C-N, a psychedelic phenethylamine, affects serotonin receptors, leading to altered perception and mood enhancement. Immediate effects include visual distortions and euphoria. Long-term use may cause persistent psychological effects such as mood disorders and cognitive impairments. Recent studies highlight its potential for inducing intense psychological experiences with associated risks.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
2C-N is a psychedelic compound, classifying it as a hallucinogen. Short-term use induces altered perceptions and euphoria, while long-term effects are not well-documented. Overdose risks include severe psychological distress and potential lasting mental health issues. Safe dosages are not well-established, with lower doses advised. Recent research focuses on its intense psychoactive effects and potential therapeutic uses. Physical effects may include dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and altered sensory perceptions.
 |
