|
Name: 4,4′-Dimethylaminorex (4,4′-DMAR; 4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-2-oxazolamine; 4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine)
Type:
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
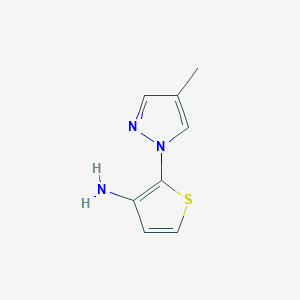
|
|
IV. History
4,4′-Dimethylaminorex (4,4′-DMAR) was first synthesized in the 1970s as a stimulant. It is a member of the amino-oxazole class of compounds and was initially studied for its psychoactive effects. Its use in recreational settings emerged in the 2000s, leading to regulatory measures due to its stimulant properties and potential for abuse.

|
|
V. Legal Information
4,4'-Dimethylaminorex is a stimulant with effects similar to amphetamines. It is controlled in the U.S. under the Federal Analog Act, reflecting its potential for abuse. Globally, it is increasingly regulated to manage stimulant misuse and reflect broader trends in synthetic stimulant control. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
4,4'-Dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) is a stimulant with effects similar to methamphetamine. It increases energy, alertness, and euphoria. It can cause dilated pupils, elevated heart rate, and increased blood pressure. Short-term effects include enhanced physical and cognitive performance, while long-term use may lead to cardiovascular issues and psychological dependence. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular problems. Safe dosing is essential, and recent research focuses on its stimulant effects and potential for abuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
4,4′-Dimethylaminorex (4,4′-DMAR) is a stimulant affecting dopamine and norepinephrine systems, leading to increased energy and euphoria. Immediate effects include heightened alertness and mood elevation, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in cognitive impairments and mood disturbances. Research highlights its stimulant properties and associated risks of psychological dependence and mental health issues.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
4,4'-Dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) is a powerful stimulant, classifying it as an upper. Short-term use increases energy and alertness, while long-term use can lead to severe psychological dependence and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe agitation, cardiovascular complications, and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are not well-established, with lower doses advised. Recent research emphasizes its high abuse potential and significant health risks. Physical effects include dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and elevated blood pressure.
 |
