|
Name: 4-dihydrotestosterone (17-beta-hydroxy-androstan-3-one)
Type:
AKA: Anabolex, Andractim, Pesomax, Stanolone

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
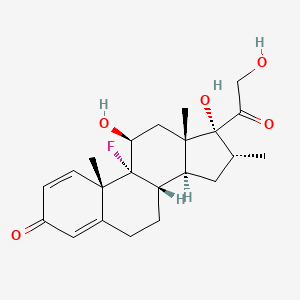
|
|
IV. History
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) was first isolated in 1940 by Dr. Elmer E. Wright, at the University of California, who worked with the U.S. Army Chemical Corps to develop a replacement for the drug testosterone. It was not until the 1970s that DHT was first isolated from the urine of women with gynecological problems.
Dihydrotestosterone is the major androgen in the male and female body and is responsible for the development of male pattern hair growth, facial hair, and male sexual characteristics. It is also responsible for the development of male breast tissue. Dihydrotestosterone is also the major androgen in the female body and is responsible for the development of female breast tissue.
The chemical structure of DHT is shown below.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent androgen that binds to the androgen receptor (AR) in the cell membrane. The and

|
|
V. Legal Information
4-Dihydrotestosterone, an anabolic steroid, is regulated as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions due to its potential for misuse in sports. In the US, it is classified under Schedule III. Globally, its use is tightly controlled to prevent abuse and manage health risks.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
4-Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent androgenic steroid that affects muscle growth and hair loss. As an upper, it enhances muscle mass and strength. Short-term effects include increased physical performance, while long-term use can lead to hair loss and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe health complications. Safe use requires medical supervision. Recent findings focus on its role in androgenic effects and potential health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
4-Dihydrotestosterone, an androgen, affects mood and aggression through androgen receptors. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and increased aggression, with long-term use potentially causing psychological issues and cognitive impairments. Research focuses on its effects on mental health and hormonal balance.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
4-Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent androgen involved in male development and secondary sexual characteristics. Historically, the understanding of hormones like DHT has been crucial in endocrinology and medicine. In modern culture, DHT is often discussed in the context of hair loss treatments, bodybuilding, and hormone replacement therapy. It plays a significant role in discussions about masculinity, aging, and health. Debates around DHT often involve its impact on hair loss, prostate health, and the ethics of hormone manipulation. Celebrities and athletes have brought attention to DHT's role in performance enhancement and aging.
 |
