|
Name: Aloin
Type: Herbal supplement
AKA: Aloe Vera, Aloe

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
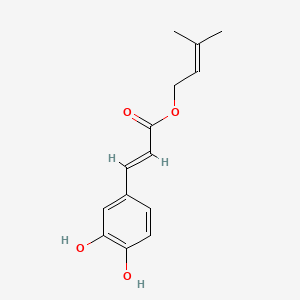
|
|
IV. History
Aloin, a compound derived from aloe vera, has been used in traditional medicine for its laxative properties for centuries. Aloe vera has a long history of use in various cultures for its healing and soothing properties, with aloin being a key component in its therapeutic applications.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Aloin is a compound found in aloe with potential medicinal properties. It is not classified as a controlled substance but is regulated in products for quality and safety. [Source: UNODC].
Key US Federal Policies:
Aloe vera products are regulated by the FDA as both over-the-counter drugs and dietary supplements. They must comply with standards for labeling and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Aloin is a compound found in aloe vera with laxative properties. It causes gastrointestinal effects such as diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Short-term use effectively treats constipation, but long-term use can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Overdose risks include severe gastrointestinal distress. Safe use involves adherence to recommended doses. Recent research highlights its effectiveness for constipation relief and potential side effects with long-term use.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Aloin, a compound from aloe vera, has minimal direct psychological effects. Immediate effects include minor mood improvement and relaxation due to its potential gastrointestinal benefits. Long-term effects are not well-documented. Research highlights its medicinal uses with limited evidence on significant psychological impacts.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Aloin, derived from aloe vera, has been used historically for its laxative and medicinal properties. It is mentioned in ancient texts from various cultures, including Egyptian and Greek. Its modern cultural significance includes its use in natural remedies and skincare products. Proponents highlight its health benefits, while opponents caution about potential side effects. Its use spans both traditional and contemporary health practices.
 |
