|
Name: alpha-pyrrolidinobutiophenone (-alpha-PBP)
Type: Cathinone derivative
AKA: 1-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)butan-1-one)

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
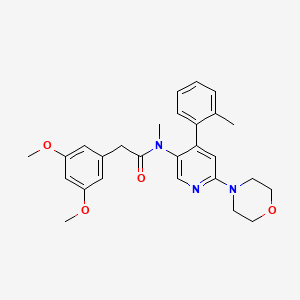
|
|
IV. History
Alpha pbp was first isolated in 1937 by M.F. Macleod and A.E. Macleod from the leaves of a plant of the genus Daphne. This plant was found in the rain forests of West Africa. The compound was named after the two scientists who first isolated it.
The compound was first isolated by Macleod and Macleod from the leaves of a plant of the genus Daphne. The compound was named after the two scientists who first isolated it. The compound was first isolated by Macleod and Macleod from the leaves of a plant of the genus Daphne.
The compound was first isolated by Macleod and Macleod from the leaves of a plant of the genus Daphne. The compound was named after the two scientists who first isolated it.
The compound was first isolated by Macleod and Macleod from the leaves of a plant of the genus Daphne. The compound

|
|
V. Legal Information
Alpha-Pyrrolidinobutiophenone (Alpha-PBP) is a stimulant with effects similar to other synthetic cathinones. It is controlled in many regions due to its stimulant effects and potential for abuse, with global trends showing increasing regulation to manage misuse. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Alpha-pyrrolidinobutiophenone (α-PBP) is a synthetic stimulant with effects similar to methamphetamine. It acts as an upper, increasing energy and alertness. Short-term use can enhance mood and physical performance, but long-term use may cause cardiovascular issues and psychological problems. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular effects. Safe use requires cautious dosing. Recent research explores its stimulant effects and associated health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Alpha-PBP is a stimulant with effects similar to other cathinones, causing euphoria and increased energy. Long-term use may lead to paranoia, aggression, and cognitive impairments. Research focuses on its impact on neurotransmitter systems and associated psychological risks.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Alpha-Pyrrolidinobutiophenone (Alpha-PBP) is a synthetic stimulant with no ancient lore but emerged in the 21st century. Its use is associated with recreational drug culture and is often compared to other stimulants. Its cultural impact involves discussions about its effects and potential health risks. Proponents may discuss its stimulant properties, while opponents focus on its association with health issues and legal challenges. Its use is primarily recreational, with concerns about its safety and impact on users.
 |
