|
Name: Amlodipine
Type: Calcium channel blocker
AKA: Norvasc

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
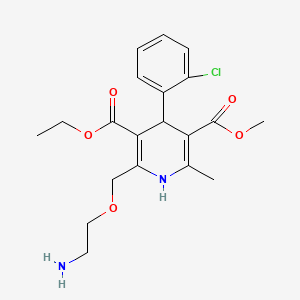
|
|
IV. History
Amlodipine was developed in the 1980s and approved for medical use in the 1990s. It is widely used for the treatment of high blood pressure and angina.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Amlodipine, a medication used for hypertension and angina, is not classified as a controlled substance. It is prescribed and regulated as a pharmaceutical agent, focusing on its use in treating cardiovascular conditions.
Key US Federal Policies:
Amlodipine is regulated by the FDA, with specific guidelines for prescription use to ensure safety and efficacy.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, is used to treat high blood pressure and angina. As a downer, it reduces blood pressure and induces vasodilation. Short-term effects include reduced blood pressure and improved heart function, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal risks. Overdose risks involve severe hypotension and potential cardiovascular issues. Safe dosing typically ranges from 5-10 mg daily. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness in managing hypertension and angina with few side effects.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, primarily affects cardiovascular function. Its psychological impacts are minimal, though some users report mood changes. Immediate effects are limited to cardiovascular improvements, with long-term use having minimal direct psychological impact. Research focuses on its cardiovascular benefits and side effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat high blood pressure and angina, classifying it as neither an upper nor a downer. Short-term use reduces blood pressure and alleviates chest pain, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal side effects. Overdose risks include severe hypotension and cardiovascular collapse. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 10 mg per day. Recent research supports its efficacy in managing hypertension and preventing cardiovascular events. Physical effects include reduced blood pressure and improved cardiac function.
 |
