|
Name: Apigenin
Type: Herbal supplement
AKA: Chamomile, Matricaria Chamomilla

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
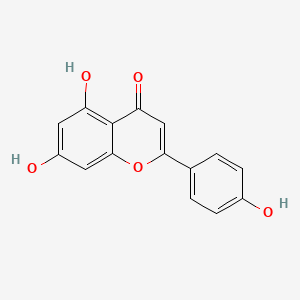
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Apigenin is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in many plants, including parsley, chamomile, and celery. Its use dates back to ancient times, where it was used for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Apigenin is studied for its potential health benefits, including anti-cancer properties and its role in promoting relaxation and sleep. Its historical use in traditional medicine highlights its importance in natural health practices.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Apigenin, a flavonoid found in various plants, is not classified as a controlled substance either globally or in the US. It is generally regarded as safe and used in dietary supplements and research. There are no significant restrictions or historical milestones affecting its legality, as it is not associated with abuse or dependence.
Key US Federal Policies:
Chamomile products are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements and must meet standards for labeling and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Apigenin, a flavonoid found in plants, is known for its calming and anti-inflammatory effects. As a downer, it can induce mild sedation and reduce anxiety. Short-term effects include relaxation and reduced inflammation, while long-term use is generally considered safe with minimal risks. Overdose is unlikely, but excessive use may cause gastrointestinal discomfort. Safe use typically involves dietary intake through fruits and vegetables. Recent research emphasizes apigenin's potential health benefits and its role in reducing stress and inflammation.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Apigenin, a flavonoid, affects neurotransmitter systems, leading to mild anxiolytic and sedative effects. Psychological impacts are generally subtle, with potential for mood improvement and reduced anxiety. Effects can last several hours, with ongoing research into its role in mental health and neuroprotection.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Apigenin, a natural flavonoid found in many plants, has been used since ancient times for its medicinal properties. Historically, it is found in chamomile, used in traditional medicine across various cultures for its calming effects. The substance has been mentioned in historical texts related to herbal medicine, reflecting its long-standing role in promoting health and wellness. In modern culture, apigenin is studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties. While it lacks the dramatic cultural impact of more potent substances, it is appreciated in wellness and natural health circles, representing the ongoing interest in plant-based remedies.
 |
