|
Name: Berberine
Type: Herbal supplement
AKA: Goldenseal, Hydrastis

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
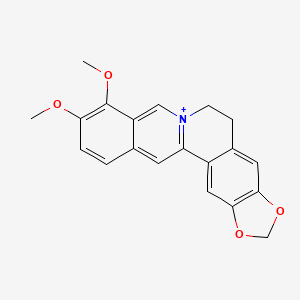
|
|
IV. History
Berberine, a natural compound found in various plants, has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It is studied for its potential health benefits, including antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Berberine, a plant alkaloid, is legally available as a dietary supplement in the US and many other countries. It is not classified as a controlled substance, allowing its use for various health benefits. Regulatory agencies like the FDA monitor its safety and efficacy, but it is generally considered safe with appropriate use. Trends indicate continued acceptance in traditional and alternative medicine.
Key US Federal Policies:
Goldenseal supplements are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements. They must meet standards for labeling, purity, and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Berberine is a natural compound used for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It acts as a downer, reducing inflammation and supporting overall health. Short-term use is generally safe and beneficial, but excessive use may cause gastrointestinal issues. Safe use involves moderate intake. Recent research highlights its effectiveness in managing metabolic conditions and supporting overall health.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Berberine, a compound with minimal psychoactive properties, affects metabolic processes rather than directly influencing mood or cognition. Some users report mild mood enhancement or cognitive effects, but these are not well-documented. Research focuses on its metabolic benefits rather than significant psychological impacts.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Berberine is an alkaloid with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, used in traditional medicine. Short-term use treats infections and inflammation, while long-term use is generally safe but may cause gastrointestinal issues. Overdose risks are low, typically leading to stomach upset. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 1500 mg per day. Recent research supports its efficacy in metabolic and cardiovascular health. Physical effects include reduced inflammation and improved metabolic function.
 |
