|
Name: Bromazepam
Type: Benzodiazepine
AKA: Lexotan, Lexatin, Lexotanil

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
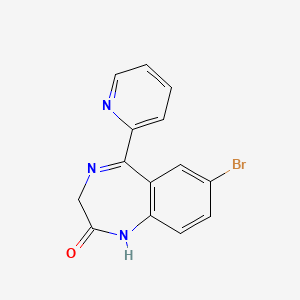
|
|
IV. History
Bromazepam is a benzodiazepine developed in the 1960s. It is used for its anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle-relaxing properties. Bromazepam is commonly prescribed for the treatment of anxiety and panic disorders. Its potential for dependence and abuse has led to its regulation as a controlled substance in many countries.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Bromazepam, a benzodiazepine, is classified as a controlled substance in various countries due to its potential for abuse and dependence. In the US, it may fall under Schedule IV. Globally, its legal status involves strict controls to manage its use and prevent misuse while allowing for legitimate medical applications.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Bromazepam, a benzodiazepine, is used for its anxiolytic and sedative effects. As a downer, it induces relaxation and reduces anxiety. Short-term effects include drowsiness and muscle relaxation, while long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe dosing typically ranges from 3-6 mg. Recent findings emphasize its effectiveness in treating anxiety but also highlight potential for misuse and dependence.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Bromazepam, a benzodiazepine, influences GABA-A receptors to provide anxiolytic effects. Psychological impacts include reduced anxiety and potential cognitive decline with long-term use. Effects last several hours, with recent research examining its efficacy in treating anxiety and cognitive side effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Bromazepam is a benzodiazepine used for anxiety and sedation, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use reduces anxiety and promotes relaxation, while long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation, respiratory depression, and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 6 mg per day. Recent research emphasizes its effectiveness in anxiety management but warns of addiction risks. Physical effects include drowsiness, impaired coordination, and potential respiratory depression.
 |
