|
Name: Butobarbital (butethal)
Type: Barbiturate
AKA: Soneryl (UK)

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
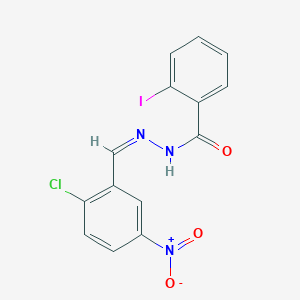
|
|
IV. History
Butobarbital, a barbiturate, was first synthesized in the 1950s. It was used for its sedative properties and has been prescribed for various medical conditions. Its history includes its role in the development of barbiturate medications and subsequent regulation due to its potential for abuse and addiction.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Butobarbital, also known as Butethal, is a barbiturate used for its sedative effects. It is controlled under Schedule IV of the Controlled Substances Act in the United States due to its potential for abuse and dependence. Regulations in other countries also focus on monitoring its use to prevent misuse. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Butobarbital (also known as butethal) is a barbiturate used as a sedative and hypnotic. It causes sedation, reduced heart rate, and impaired motor function. Short-term use is effective for sleep disorders, but long-term use can lead to dependence, cognitive impairment, and significant health issues. Overdose risks include severe sedation, respiratory depression, and potential death. Safe use involves precise dosing and medical supervision. Recent research emphasizes its efficacy and risks associated with prolonged use.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Butobarbital, a barbiturate, enhances GABA-A receptor activity, leading to sedation and anxiolysis. Immediate effects include relaxation and decreased anxiety, lasting several hours. Long-term use can result in cognitive impairments, dependence, and mood disturbances. Research highlights the risks of cognitive decline and psychological dependence associated with chronic barbiturate use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Butobarbital, also known as Butethal, is a barbiturate used for its sedative and hypnotic effects. Its cultural significance lies in its historical use as a sleep aid and its potential for abuse. Media coverage often discusses its risks, including addiction and overdose. Butobarbital is used both recreationally and medicinally, contributing to discussions about barbiturate use and drug regulation.
 |
