|
Name: Cannabidiol
Type: Cannabis derivative
AKA: CBD

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
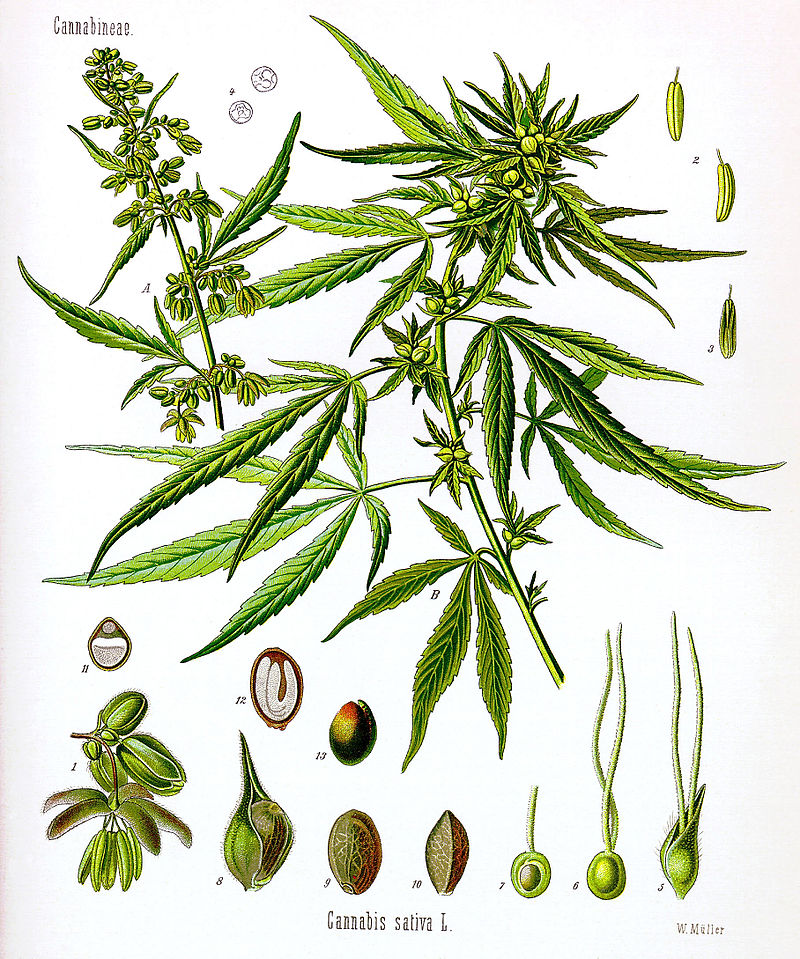
|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
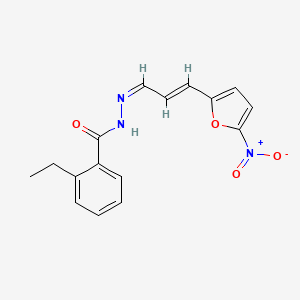
|
|
IV. History
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It has gained significant attention for its potential therapeutic benefits, including the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety, and pain. CBD has been legalized in many parts of the world and is available in various forms, including oils, edibles, and topical products. Its growing popularity reflects the increasing acceptance of cannabis-based therapies.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Cannabidiol (CBD) is increasingly regulated globally due to its non-psychoactive properties and therapeutic potential. In the US, CBD derived from hemp with less than 0.3% THC is legal under the 2018 Farm Bill. Globally, its legal status varies, with many countries allowing CBD use in medical or therapeutic contexts while regulating THC content.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive component of cannabis, is used for its therapeutic effects. As a health supplement, it supports anxiety relief and pain management without inducing a high. Short-term effects include reduced anxiety and improved sleep, while long-term use is generally safe. Overdose risks are minimal, but excessive use may cause gastrointestinal discomfort. Safe dosing typically ranges from 5-50 mg daily. Recent research emphasizes its potential therapeutic benefits and minimal side effects.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, interacts with endocannabinoid receptors, leading to mood stabilization and anxiety reduction. Psychological effects include improved mood and cognitive function, with potential therapeutic benefits for depression and anxiety. Effects are generally subtle, with ongoing research into its efficacy for various mental health conditions and overall impact on cognition.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive compound derived from cannabis, used for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic properties, classifying it as neither an upper nor a downer. Short-term use reduces pain, anxiety, and inflammation, while long-term use is generally considered safe with minimal side effects. Overdose risks are low, with large doses typically leading to drowsiness. Safe dosages vary widely, with typical use around 20-40 mg per day. Recent research supports its efficacy in treating various conditions, including epilepsy and anxiety disorders. Physical effects include reduced pain, lower anxiety, and improved sleep.
 |
