|
Name: Cannabis Sativa
Type: Cannabis
AKA: Marijuana, Weed, Green, Herb, Chronic, Ganja, Loud, Fire, Dank

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
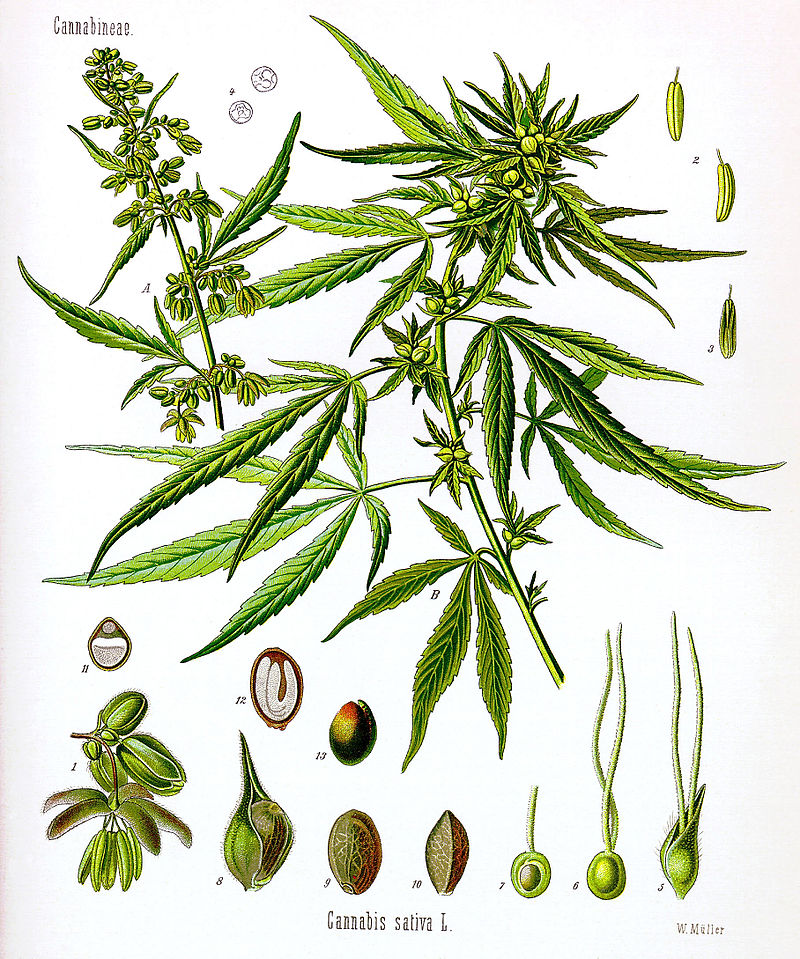
|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
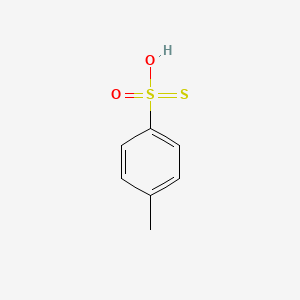
|
|
IV. History
Cannabis Sativa, a plant with psychoactive properties, has been used for thousands of years in various cultures for medicinal, recreational, and industrial purposes. Its historical use spans from ancient civilizations to contemporary medicine and recreational use.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Cannabis sativa is a plant used for its psychoactive and medicinal properties. It is regulated differently across the globe, with some regions allowing medical use while others maintain strict controls. The trend is towards increasing regulation to manage both medical and recreational use. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Cannabis sativa is a plant used both recreationally and medicinally. It acts as an upper, with effects including euphoria and altered perception. Short-term use can enhance mood and appetite, while long-term use may cause respiratory issues, dependency, and cognitive effects. Overdose risks are generally low but may include severe psychological effects. Safe use involves moderate consumption and awareness of its effects. Recent research supports its medicinal benefits and examines its potential health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Cannabis sativa, containing THC and CBD, affects cannabinoid receptors, leading to altered perception, euphoria, and relaxation. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and sensory distortions, lasting several hours. Long-term use may lead to cognitive impairments, mood disturbances, and potential dependence. Research highlights its therapeutic uses and associated risks of mental health issues and dependence.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Cannabis sativa is a widely used psychoactive plant, producing both stimulant and depressant effects depending on the strain, classifying it as both an upper and a downer. Short-term use can induce euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception, while long-term use may lead to cognitive impairment and psychological dependence. Overdose is rare but can cause severe anxiety and paranoia. Safe usage varies, with recommended dosages generally under 10 mg of THC. Recent research explores its therapeutic potential and abuse risks. Physical signs include red eyes, dry mouth, and altered mental state.
 |
