|
Name: Cathine
Type: Stimulant
AKA: Khat, Kat, (+)-norpseudoephedrine

|
|
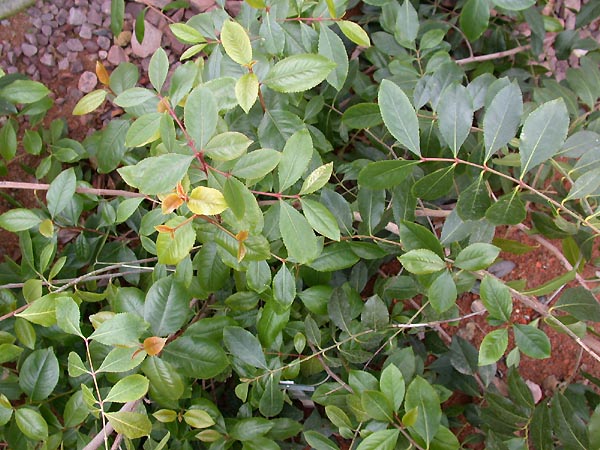
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
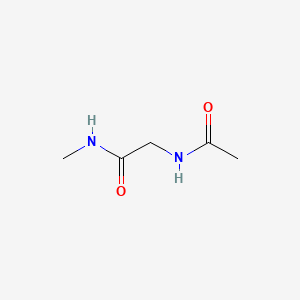
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Cathine, a stimulant found in the khat plant, has been used in East Africa and the Arabian Peninsula for centuries. It is studied for its psychoactive effects and its role in traditional practices.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Cathine, a stimulant found in khat, is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the US, reflecting its potential for abuse but accepted medical use. It is legal in some countries where khat chewing is culturally significant, but banned or restricted in others. The UNODC highlights the need for balanced regulation to respect cultural practices while preventing misuse and health risks.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Cathine is a stimulant found in the khat plant, related to cathinone. It increases heart rate and blood pressure. Short-term use may enhance alertness and energy, while long-term use can lead to psychological problems and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe agitation, cardiovascular effects, and potential death. Safe use requires careful dosing and monitoring. Recent research highlights its stimulant effects and associated health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Cathine, a stimulant, affects dopamine and norepinephrine systems, leading to increased alertness and mood enhancement. Immediate effects include improved mood and energy, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in cognitive impairments and mood disturbances. Research highlights its stimulant effects and associated risks of psychological dependence.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Cathine is a stimulant derived from the khat plant, used traditionally in East Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Its historical use includes cultural and social contexts, where it has been consumed for its stimulant effects. In modern times, it is studied for its potential medical uses. Proponents highlight its stimulating effects, while opponents caution about potential abuse and health risks. Its use spans both traditional and modern contexts.
 |
