|
Name: Chlordiazepoxide
Type: Benzodiazepine
AKA: Librium, Libritabs, Limbitrol, SK-Lygen

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
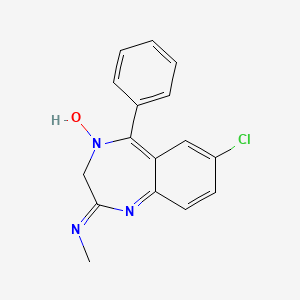
|
|
IV. History
Chlordiazepoxide, the first benzodiazepine, was discovered in 1957 by Leo Sternbach at Hoffmann-La Roche and introduced in 1960 as Librium. It revolutionized the treatment of anxiety, offering a safer alternative to barbiturates. Its development marked a significant milestone in psychopharmacology, leading to the creation of many other benzodiazepines. Chlordiazepoxide was widely used for anxiety and alcohol withdrawal but has largely been replaced by newer benzodiazepines with improved safety profiles.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Chlordiazepoxide, a benzodiazepine used for anxiety and alcohol withdrawal, is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the US. Globally, it is regulated similarly, reflecting concerns about its potential for dependence and abuse while allowing for its medical use under strict conditions.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Chlordiazepoxide is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal symptoms. It causes sedation, reduced heart rate, and impaired motor function. Short-term use is effective for anxiety management, but long-term use can lead to dependence, cognitive impairment, and significant health issues. Overdose risks include severe sedation, respiratory depression, and potential death. Safe use involves following prescribed dosages. Recent research explores its efficacy in treating anxiety and alcohol withdrawal, highlighting associated risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Chlordiazepoxide, a benzodiazepine, enhances GABA-A receptor activity, providing anxiolytic and sedative effects. Psychological impacts include reduced anxiety and improved mood, with long-term use carrying risks of cognitive decline and dependence. Research examines its use for anxiety disorders and potential cognitive side effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Chlordiazepoxide, the first benzodiazepine, has significant cultural importance as it marked the beginning of a new era in anxiety and sedation treatment. Its introduction in the 1960s revolutionized the treatment of anxiety disorders, leading to the widespread use of benzodiazepines. Chlordiazepoxide represents the development of safer alternatives to barbiturates, contributing to the broader understanding of anxiolytics and their role in mental health. Its historical significance is reflected in its influence on psychiatric treatment and the ongoing discourse about benzodiazepine use and dependency.
 |
