|
Name: Clopidogrel
Type: Antiplatelet agent
AKA: Plavix

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
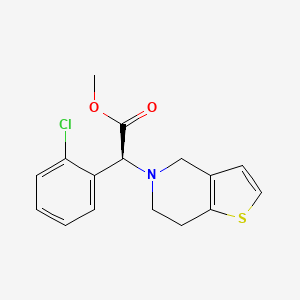
|
|
IV. History
Clopidogrel, an antiplatelet medication, was developed in the 1990s. It is used to prevent blood clots in cardiovascular diseases. Its development represents a significant advancement in the prevention of stroke and heart attacks, with its use becoming widespread in modern cardiology.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Clopidogrel is a prescription medication used to prevent blood clots. It is not classified as a controlled substance but is regulated due to its medical use. Globally, it is prescribed with specific guidelines to ensure safety. Trends focus on its effective use in preventing cardiovascular events, with no significant movement towards increased regulation. [Source: UNODC].
Key US Federal Policies:
Clopidogrel is regulated by the FDA, with specific guidelines for prescription use to ensure safety and efficacy.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet medication used to prevent blood clots. It inhibits platelet aggregation, acting as a preventive agent rather than an upper or downer. Short-term use reduces the risk of stroke and heart attack, while long-term use is generally safe with monitored dosing. Overdose risks include bleeding complications. Safe use involves adherence to prescribed doses and monitoring for bleeding issues. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and safety in preventing cardiovascular events.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Clopidogrel does not have psychoactive effects. Its primary action is to prevent blood clots, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes, and improving overall cardiovascular health.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Clopidogrel, an antiplatelet medication, has no historical or cultural lore, being a recent development. It is widely used to prevent blood clots in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Its cultural significance lies in its impact on public health, with millions of people benefiting from its use in preventing heart attacks and strokes. Proponents include medical professionals and patients, while there are no significant opponents. Its use is strictly medicinal, reflecting its importance in modern cardiovascular care and its role in improving patient outcomes.
 |
