|
Name: Codeine
Type: Opioid
AKA: Morphine methyl ester, methyl morphine
|
|
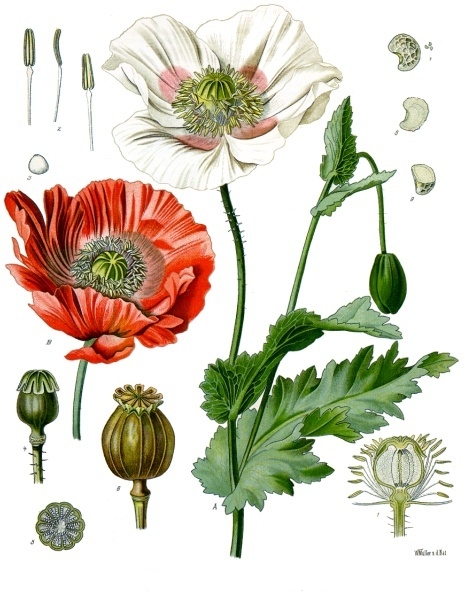
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
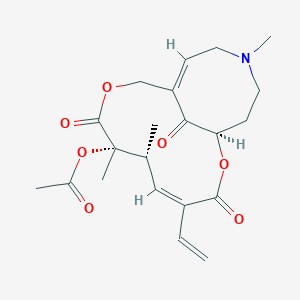
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Codeine, derived from opium, has been used as a cough suppressant and pain reliever since the 19th century. It is commonly prescribed for mild to moderate pain and cough suppression. Codeine's use is widespread, though it is regulated due to potential for addiction and abuse.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Codeine, an opioid used for pain relief and cough suppression, is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions due to its potential for abuse. Its legal status reflects efforts to manage opioid use and prevent misuse.
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Codeine, an opioid analgesic, has been used since the early 19th century for pain relief and cough suppression. It acts as a downer, causing sedation and analgesia. Physical impacts include respiratory depression, decreased heart rate, and constricted pupils. Short-term use is effective for managing pain and cough, but long-term use may lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use requires careful dosing and medical supervision. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and safety compared to other opioids.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Codeine, an opioid, impacts opioid receptors to provide analgesia and mood alteration. Immediate effects include euphoria and cognitive impairment, while long-term use may lead to dependence and psychological issues. Research examines its efficacy and abuse potential.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Codeine is an opioid used for pain relief and cough suppression, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use alleviates moderate pain and reduces coughing, while long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose is possible and can result in respiratory depression and death. Safe dosages are typically under 60 mg per dose, with a maximum of 240 mg per day. Recent findings emphasize caution in prescribing due to addiction risks. Physical effects include drowsiness, constipation, and constricted pupils.
 |
