|
Name: Collagen
Type: Protein Supplement
AKA: Collagen protein, connective tissue protein

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
Collagen
|
|
IV. History
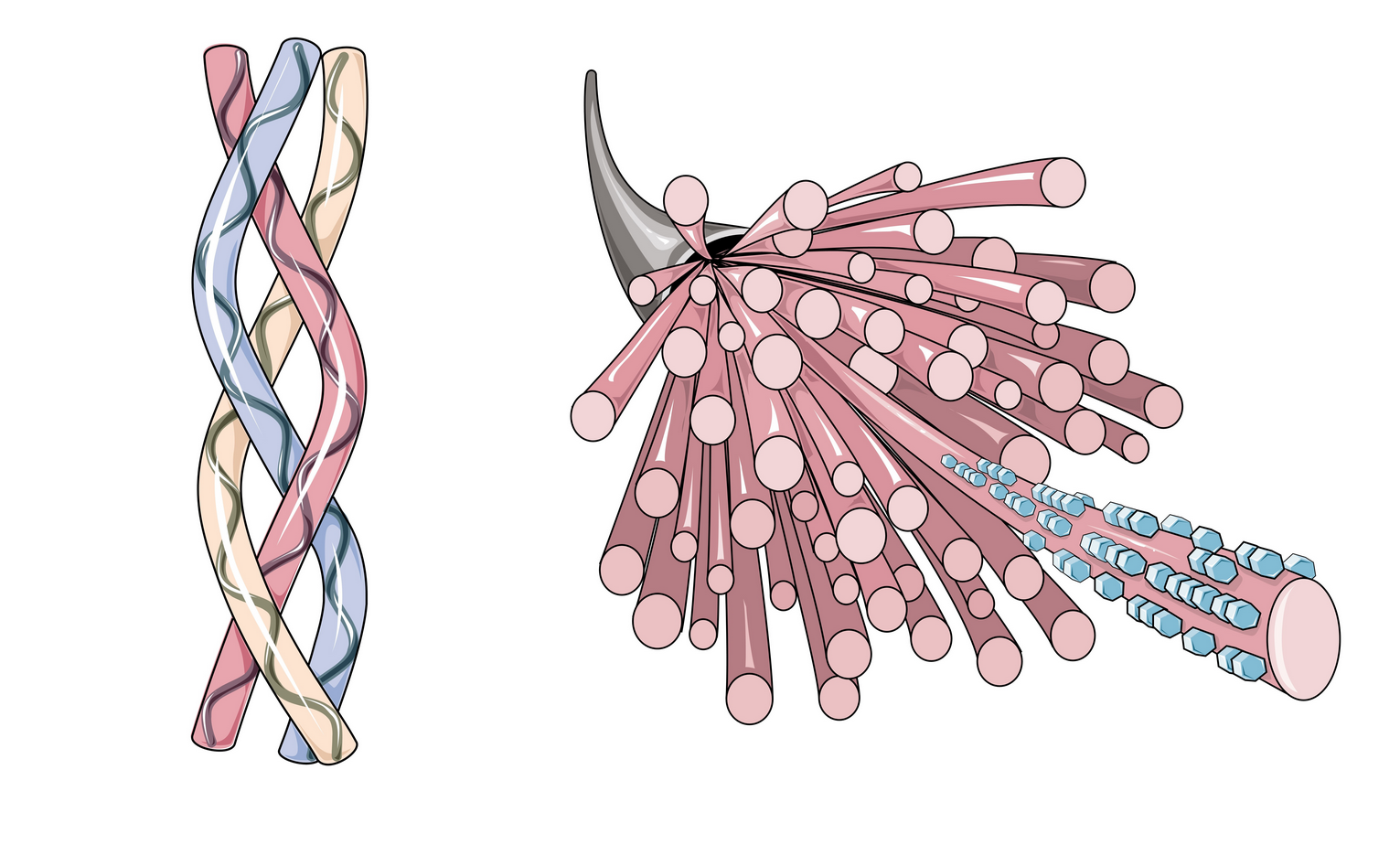
Collagen, a protein found in connective tissues, has been used in medical and cosmetic applications since the early 20th century. Its uses have expanded from skin treatments to various medical and aesthetic applications.

|
|
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Collagen is a protein that supports skin, bones, and connective tissues. It is generally considered safe and does not cause significant physical damage. Short-term use can improve skin elasticity and joint health. Long-term use is safe, but excessive intake might lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. Safe amounts vary, but it is generally recommended to follow dosage instructions. Recent studies highlight its benefits in maintaining skin and joint health.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Collagen is generally used for physical health benefits rather than psychological effects. There is limited research on its direct impact on mood or cognition, though it supports overall health which may indirectly affect psychological well-being.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Collagen is a natural protein used for its structural and regenerative properties in skin, joints, and connective tissues. Short-term use improves skin elasticity and joint function, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal side effects. Overdose risks are low, typically leading to gastrointestinal upset. Safe dosages vary, with typical use around 2.5-15 grams per day. Recent research supports its efficacy in skin health and joint function improvement. Physical effects include improved skin elasticity and joint health.
 |
