|
Name: Crotonyl fentanyl ((E)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylbut-2-enamide)
Type: Synthetic opioid
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
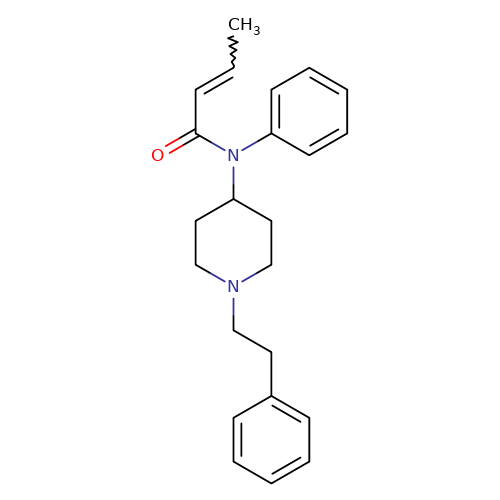
|
|
IV. History
Crotonyl Fentanyl, a potent synthetic opioid, was introduced in the early 21st century. It is used primarily in research to study its effects on opioid receptors. Its history reflects the ongoing development of synthetic opioids and their implications for pain management and drug policy.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Crotonyl fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid, and its legal status is subject to strict controls globally. In the U.S., it is regulated under the Federal Analog Act due to its similarity to fentanyl, a Schedule II controlled substance. Internationally, many countries have classified it as a controlled substance to prevent misuse. The trend is toward increasingly stringent controls to combat the opioid crisis. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Crotonyl fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid used for pain relief. It acts as a downer, causing significant sedation and respiratory depression. Short-term use can manage pain effectively, but long-term use may lead to addiction and tolerance. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use requires precise dosing and medical supervision. Recent research examines its potency and safety compared to other opioids.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Crotonyl fentanyl, an opioid, affects opioid receptors, causing euphoria and cognitive impairment. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and pain relief, lasting several hours. Long-term use can lead to dependence and psychological issues such as depression. Research indicates significant mental health risks with chronic use, including severe mood disturbances and potential for addiction.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Crotonyl fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid providing pain relief, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use alleviates severe pain, while long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks are extremely high, causing respiratory depression and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are strictly prescribed, often in microgram quantities. Recent research underscores its potency and associated risks of misuse. Physical effects include drowsiness, constricted pupils, and respiratory depression.
 |
