|
Name: Dichloralphenazone
Type: Barbiturate
AKA: Midrin, dichloralantipyrine
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
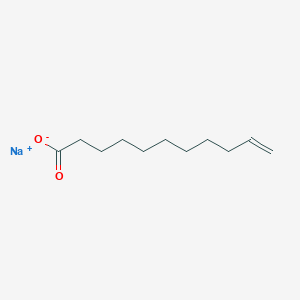
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Dichloralphenazone, a sedative and hypnotic, was developed in the mid-20th century. It was used to treat insomnia and anxiety but is less commonly used today due to the development of safer alternatives.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Dichloralphenazone is a sedative and hypnotic used to manage insomnia. It is controlled in some regions due to its potential for abuse and dependence. Global trends show increasing regulation to prevent misuse and manage its impact on health. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Dichloralphenazone is a sedative and analgesic used to treat pain and insomnia. It causes sedation and reduces anxiety, acting as a downer. Short-term use is effective for managing pain and sleep disorders, but long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe use involves following prescribed dosages and monitoring for side effects. Recent research explores its effectiveness and compares it with other sedatives.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Dichloralphenazone, a sedative and analgesic, affects GABA receptors, causing sedation and mood alteration. Immediate effects include anxiety reduction and mood enhancement, while long-term use can result in dependence and psychological issues such as depression. Effects last several hours, with risks of significant mental health disturbances with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Dichloralphenazone is a sedative and analgesic used in the treatment of headaches, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use reduces headache symptoms and induces relaxation, while long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 100 mg per day. Recent findings emphasize cautious use due to addiction potential. Physical effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination.
 |
