|
Name: Diethylthiambutene
Type: Narcotic
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
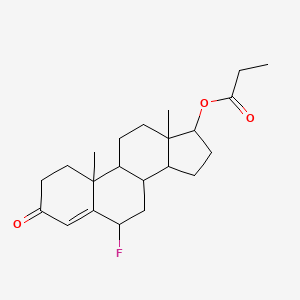
|
|
IV. History
Diethylthiambutene, a synthetic opioid, was first developed in the 1950s. It was researched for its potent analgesic properties and potential as a pain management drug. Although it has not achieved widespread use, it remains a point of interest in studies exploring opioid analgesics and their effects. Its historical significance lies in its contribution to the understanding of opioid receptor interactions and pain management options.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Diethylthiambutene, a sedative and anxiolytic, is classified as a controlled substance due to its potential for abuse. Its status reflects regulations aimed at managing its use and preventing misuse.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Diethylthiambutene is a barbiturate used as a sedative and anxiolytic. As a downer, it induces sedation and relaxation. Short-term effects include reduced anxiety and improved sleep, while long-term use may lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks involve severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe dosing requires medical supervision. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and potential risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Diethylthiambutene, a barbiturate, affects GABA-A receptors to provide sedation and mood alteration. Immediate effects include relaxation and cognitive impairment, while long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive decline. Research shows risks of severe mental health disturbances and psychological dependence with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Diethylthiambutene is a sedative, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use induces sedation and relaxation, while long-term use can lead to dependence, tolerance, and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation, respiratory depression, and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosages are typically prescribed by medical professionals. Recent research highlights its effectiveness in sedation but warns of potential dependence and overdose risks. Physical effects include drowsiness, impaired coordination, and respiratory depression.
 |
