|
Name: Difenoxin 1 mg/25 ug AtSO4/du
Type: Antidiarrheal
AKA: Motofen

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
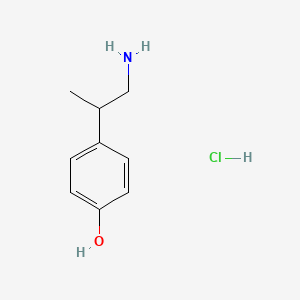
|
|
IV. History
Difenoxin, an opioid, was developed in the mid-20th century as a treatment for diarrhea. Its history reflects its role in medical treatment and its transition to controlled status due to potential abuse and addiction risks.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Difenoxin is an opioid used to treat diarrhea. Its preparations are controlled due to potential for abuse and addiction. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Difenoxin is used to manage diarrhea, functioning similarly to diphenoxylate. It causes reduced gastrointestinal motility, sedation, and constricted pupils. Short-term use is effective for diarrhea relief, but long-term use may result in constipation and potential dependency. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use involves adherence to prescribed doses. Recent research highlights its effectiveness and opioid-like properties.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Difenoxin, an antidiarrheal with opioid properties, affects mu-opioid receptors, producing mild euphoria and sedation. Immediate effects include decreased gastrointestinal motility and mood enhancement, lasting a few hours. Long-term use can lead to dependence, cognitive impairments, and mood swings. Recent studies emphasize the risks of psychological dependence and potential cognitive effects with prolonged use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Difenoxin is used as an antidiarrheal medication. Its cultural significance is tied to its role in managing diarrhea and gastrointestinal conditions. Media coverage often highlights its effectiveness and the risks associated with its use. Difenoxin is used medicinally and is part of broader discussions about gastrointestinal health and treatment options for diarrhea.
 |
