|
Name: Dimethyltryptamine
Type: Psychedelic
AKA: DMT

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
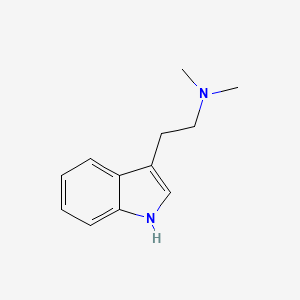
|
|
IV. History
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), a powerful psychedelic, has been used in traditional Amazonian practices for centuries. Its synthetic form has been studied in modern research for its psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic applications.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), a powerful psychedelic, is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the US, making it illegal. Many countries have similarly banned it due to its potent psychoactive effects. The UNODC highlights the need for strict regulation of psychedelics to prevent misuse. Some places, like Brazil, allow its use in traditional religious ceremonies.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a powerful hallucinogen found in various plants. It induces intense hallucinations and altered states of consciousness, acting as a psychoactive upper. Short-term use can lead to profound psychological experiences, while long-term use may cause psychological risks or hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD). Overdose risks are minimal, but improper use can lead to severe psychological distress. Safe use involves a controlled environment and cautious dosing. Recent research explores its potential therapeutic uses.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
N/A
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a powerful hallucinogen with significant cultural and spiritual significance. Its cultural use is linked to various religious and shamanic practices. Media coverage often addresses its effects, legal status, and potential for abuse. DMT is used both recreationally and in spiritual contexts, contributing to discussions about psychedelics and their role in culture.
 |
