|
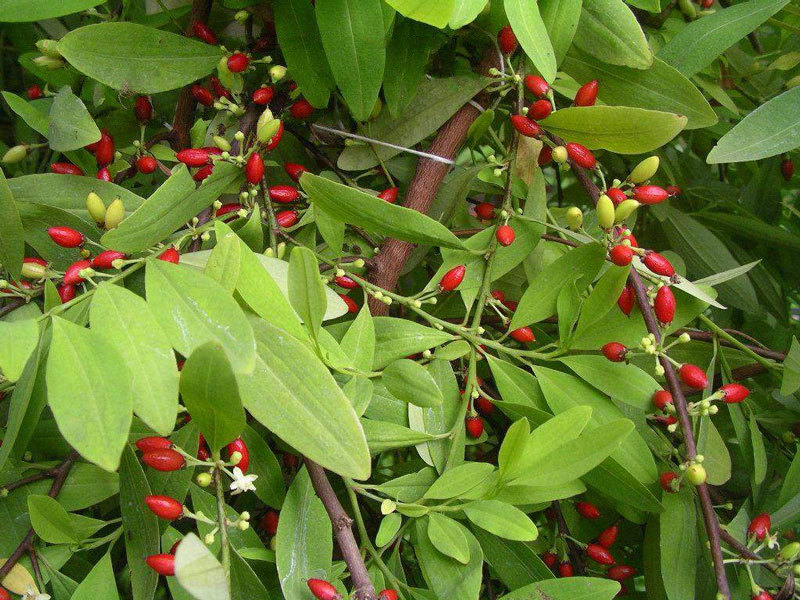
Name: Ecgonine
Type: Stimulant
AKA: Cocaine precursor, in Coca leaves

|
|
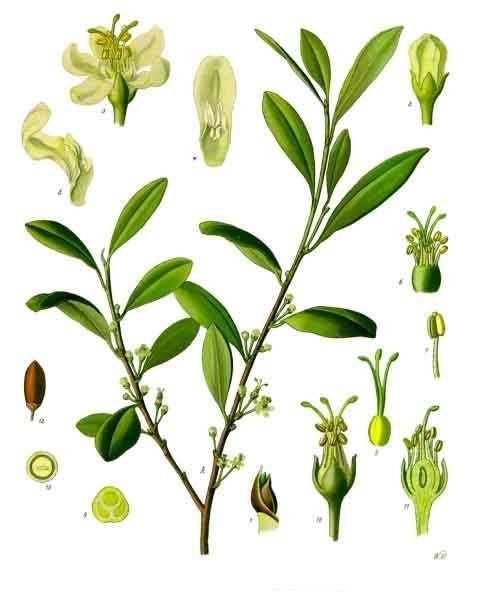
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Ecgonine, a compound derived from coca leaves, was identified in the late 19th century. It is a precursor in the synthesis of cocaine. Its historical role is significant in the development of cocaine and its derivatives, impacting both medical use and recreational drug culture.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Ecgonine is a tropane alkaloid derived from coca plants, used as a precursor in the synthesis of cocaine. It is controlled due to its association with cocaine production. In the U.S., it is regulated under federal laws concerning precursor chemicals. Internationally, ecgonine's status is also tightly controlled as part of broader efforts to combat cocaine trafficking. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Ecgonine is a natural alkaloid found in coca leaves and is a precursor to cocaine. It acts as a central nervous system stimulant, increasing heart rate and blood pressure, thus an upper. Short-term effects include euphoria and increased energy, while long-term use can cause cardiovascular issues and addiction. Overdose risks include severe cardiovascular events and neurological damage. Safe use is not well-defined due to its role as a precursor, but high doses should be avoided. Recent research focuses on its role in cocaine production.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
N/A
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Ecgonine is a naturally occurring alkaloid found in coca leaves, classifying it as a stimulant. Short-term use can increase energy and alertness, while long-term use is associated with potential dependence and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks are relatively low but may include severe agitation and cardiovascular problems. Safe dosages are not well-established, with lower doses advised. Recent research focuses on its role in the synthesis of cocaine. Physical effects include increased heart rate and blood pressure, with potential for dependency.
 |
