|
Name: Fenethylline
Type: Stimulant
AKA: Captagon, amfetyline, ethyltheophylline amphetamine

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
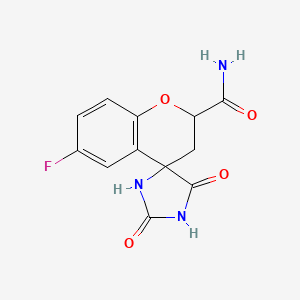
|
|
IV. History
Fenethylline, a stimulant and amphetamine analog, was developed in the 1960s. It was used for its stimulating effects but is now banned in many countries due to its potential for abuse and addiction. It was used primarily in the treatment of attention deficit disorders.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Fenethylline is a stimulant with potential for abuse. It is controlled under stimulant laws due to its effects on mental health and potential for addiction. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Fenethylline is a stimulant and the active ingredient in the drug Captagon. It causes increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and dilated pupils. Short-term use provides enhanced alertness and energy, while long-term use may lead to cardiovascular issues and addiction. Overdose risks include severe cardiovascular effects and potential death. Safe use requires careful dosing and medical supervision. Recent research highlights its stimulant effects and associated risks with abuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Fenethylline, a stimulant combining amphetamine and theophylline, produces euphoria, increased alertness, and enhanced sociability. Immediate psychological effects include mood elevation, increased sociability, and anxiety. Long-term use can lead to dependence, anxiety disorders, and cognitive impairments. Chronic use is associated with mood swings and potential psychiatric disorders. Recent research indicates risks of severe anxiety and paranoia.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Fenethylline is a stimulant with amphetamine-like effects, historically used in the treatment of attention deficit disorders. Its cultural significance is related to its role in stimulant use and the history of stimulant medications. Media coverage often focuses on the historical and contemporary use of stimulants and their effects on mental health. Fenethylline is used medicinally rather than recreationally and is part of broader discussions about stimulant use and treatment for attention disorders.
 |
