|
Name: Flavonoids and Procyanidins
Type: Nutritional supplement
AKA: Hawthorn, Crataegus

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
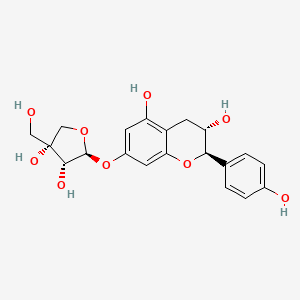
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Flavonoids and procyanidins are plant compounds with antioxidant properties, used for centuries in traditional medicine. They are found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Their health benefits have been recognized in modern research, contributing to their use in dietary supplements.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Flavonoids and procyanidins are compounds found in various fruits and vegetables, known for their antioxidant properties. They are generally not controlled substances and are legal in most countries. Regulations focus on their use in dietary supplements and food products to ensure safety and efficacy. [Source: UNODC].
Key US Federal Policies:
Hawthorn supplements are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements. They must meet standards for labeling, purity, and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Flavonoids and procyanidins are plant compounds with antioxidant properties. They act as upper, supporting cellular health and reducing inflammation. Short-term use is generally safe and beneficial, but excessive consumption may cause gastrointestinal issues. Safe use involves moderate intake. Recent research highlights their potential health benefits and role in preventing chronic diseases.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Flavonoids and procyanidins, found in various fruits and vegetables, support cognitive function and mood regulation. Immediate effects include improved mood and cognitive performance. Long-term consumption is associated with reduced risk of cognitive decline and mood disorders. Research highlights their role in brain health and potential benefits for mental well-being.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Flavonoids and procyanidins are plant compounds with antioxidant properties. Their cultural significance lies in their health benefits and use in dietary supplements. Media coverage often highlights their role in promoting cardiovascular health and reducing inflammation. These substances are used both in dietary contexts and for medicinal purposes, contributing to discussions about nutrition and health.
 |
