|
Name: Fludiazepam
Type: Benzodiazepine
AKA: Flunitazene

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
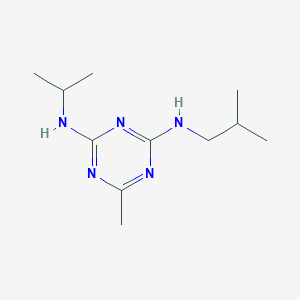
|
|
IV. History
Fludiazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative developed in the 1970s. It is used for its anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle-relaxing properties. Fludiazepam is less commonly prescribed compared to other benzodiazepines, but it remains an important option for certain medical conditions. Its use is regulated due to the potential for dependence and abuse.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Fludiazepam, a benzodiazepine, is classified as a controlled substance in many countries due to its potential for abuse and dependence. In the US, it may be regulated as a Schedule IV drug. Globally, it faces similar controls, with regulatory trends focused on preventing misuse while allowing for legitimate medical use.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Fludiazepam, a benzodiazepine, is used for its anxiolytic and sedative effects. As a downer, it induces relaxation and reduces anxiety. Short-term effects include drowsiness and muscle relaxation, while long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe dosing typically ranges from 2-10 mg. Recent findings emphasize its effectiveness in treating anxiety but also note concerns over dependence and misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Fludiazepam, a benzodiazepine, influences GABA-A receptors, resulting in anxiolytic and sedative effects. Psychological effects include reduced anxiety and impaired cognition. Long-term use can cause dependence and cognitive decline. Recent studies focus on its efficacy in treating anxiety and its potential cognitive side effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Fludiazepam is a benzodiazepine used for its anxiolytic and sedative effects. The history of benzodiazepines includes their development for treating anxiety, insomnia, and other conditions. Fludiazepam's cultural significance is tied to the broader narrative of mental health treatment and the evolving understanding of anxiety disorders. The use of benzodiazepines is often debated, with discussions about their benefits, risks, and potential for dependence. Media coverage frequently highlights personal experiences with these medications, contributing to ongoing conversations about mental health care, the ethics of pharmaceutical treatment, and the pursuit of safer therapeutic options.
 |
