|
Name: Folic Acid
Type: Vitamin
AKA: Vitamin B9, Folate, Pteroylglutamic acid, Folacin

|
|
II. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
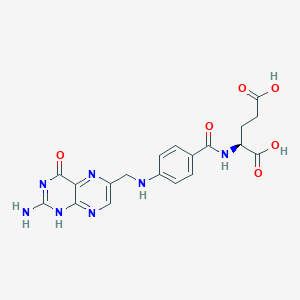
|
|
III. History
Folic acid, a B vitamin, has been used since the early 20th century to prevent deficiencies and treat anemia. It is vital for DNA synthesis and is used in prenatal vitamins to prevent birth defects.
|
|
IV. Legal Information
Folic acid is legal and widely available as a dietary supplement in the United States and many other countries. In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandated the fortification of enriched grain products with folic acid in 1998 to reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
|
|
V. Physiological Effects
Folic acid is crucial for DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation. It plays a vital role in the formation of red blood cells and is essential for proper brain function and mental health. Adequate folic acid intake is particularly important during periods of rapid growth such as pregnancy, infancy, and adolescence.
 |
|
VI. Culture
Folic acid has been used for decades to prevent neural tube defects and support overall health. It is mentioned in medical literature and has a significant cultural impact due to its role in prenatal care and dietary health. Proponents highlight its importance in preventing birth defects and supporting bodily functions, while opponents may question its effectiveness in certain contexts. Its use is both medicinal and preventive.
 |