|
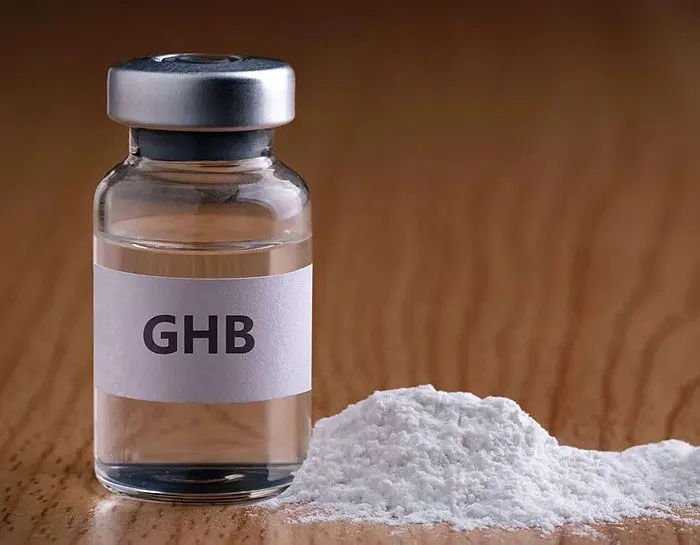
Name: GHB
Type: Sedative
AKA: Gamma Hydroxybutyric Acid, gamma hydroxybutyrate, sodium oxybate

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) was first synthesized in the 1960s. Initially studied for its potential medical uses, GHB gained popularity as a recreational drug. Its use has led to significant regulatory scrutiny and public health concerns, particularly regarding its potential for abuse and overdose.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB), a central nervous system depressant, is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the US for non-medical use, but has approved medical uses as a Schedule III substance. It is similarly regulated in many countries due to its potential for abuse. The UNODC emphasizes the need for balanced regulation to ensure safe medical use while preventing misuse.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) is a central nervous system depressant that induces sedation, euphoria, and muscle relaxation. It can cause drowsiness, reduced heart rate, and respiratory depression. Short-term effects include relaxation and mood enhancement, while long-term use may lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks involve severe sedation and potential death. Safe use requires careful dosing. Recent research focuses on its use as a therapeutic agent and risks of misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
GHB is a central nervous system depressant with sedative and euphoric effects. Short-term use can enhance mood and relaxation, while long-term use may lead to dependence, cognitive impairments, and mood disorders. Research highlights its impact on GABA and glutamate systems.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
GHB (Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate) is a central nervous system depressant used medically for narcolepsy and abused recreationally for its euphoric and sedative effects. The history of GHB includes its use in medical settings, its popularity in the club and party scene, and its association with cases of drug-facilitated sexual assault. GHB's cultural significance lies in its dual role as a therapeutic agent and a recreational drug with significant abuse potential. Media coverage often focuses on its dangers, legal status, and the challenges of balancing its medical uses with the risks of misuse and criminal activity.
 |
