|
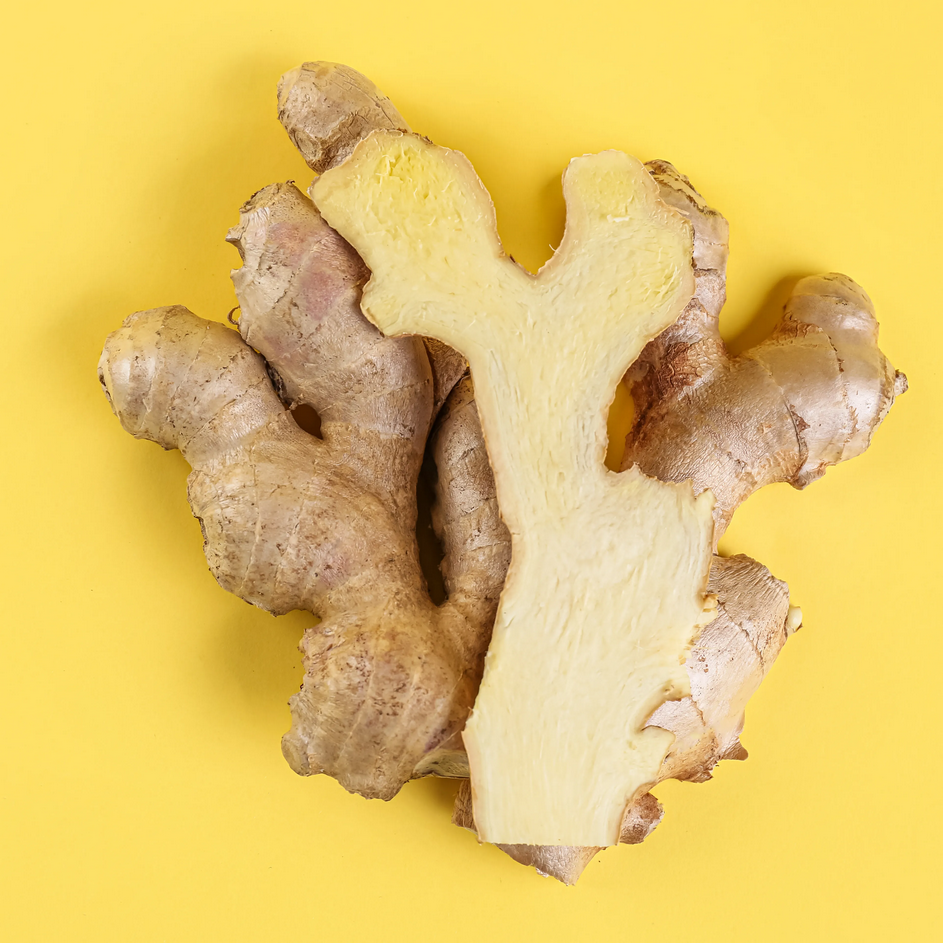
Name: Ginger
Type: Medicinal Herb
AKA: Zingiber officinale

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
|
IV. History
Ginger, a spice with medicinal properties, has been used for over 2,000 years in traditional medicine. Originating in Southeast Asia, it is valued for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits and remains widely used in culinary and therapeutic applications.

|
|
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Ginger is a common spice known for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits. It is generally safe and has minimal adverse effects. Short-term use is effective for nausea and inflammation, with long-term use being safe for most people. Risks of overdose are low, though excessive amounts may cause digestive discomfort. Safe use involves moderate consumption. Recent research highlights its anti-inflammatory properties and benefits for digestive health.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Ginger, a natural herb, has mild psychoactive effects. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and sensory relaxation. Long-term use is associated with general well-being and minor psychological benefits. Research emphasizes its therapeutic properties and limited psychological impact.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Ginger is a spice used in cooking and traditional medicine. Its cultural significance lies in its use for its flavor and health benefits. Media coverage often highlights its benefits for digestion, inflammation, and other health conditions. Ginger is used both in culinary and medicinal contexts, contributing to discussions about diet, health, and traditional remedies.
 |
