|
Name: Gingerol
Type: Herbal supplement
AKA: Ginger, Zingiber

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
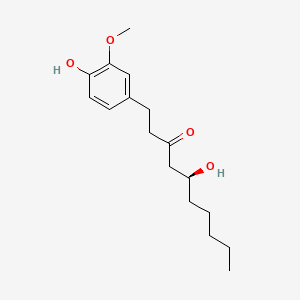
|
|
IV. History
Gingerol, a compound found in ginger, has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and has been studied for its potential health benefits in various conditions.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Gingerol, a bioactive compound found in ginger, is not classified as a controlled substance. It is regulated as a dietary supplement or pharmaceutical agent due to its health benefits.
Key US Federal Policies:
Ginger supplements are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements. They must meet standards for labeling, purity, and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Gingerol, derived from ginger, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. As an upper, it supports cognitive function and may improve mood. Short-term effects include reduced inflammation and improved digestion, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal risks. Overdose risks are minimal but may include gastrointestinal issues. Safe dosing is typically guided by a healthcare provider. Recent research focuses on its health benefits and potential applications.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Gingerol, a compound in ginger, influences neurotransmitter systems with potential mood-enhancing effects. Immediate effects include improved mood and reduced anxiety, with benefits potentially lasting longer. Long-term use is generally considered safe, with limited research indicating potential psychological benefits and minimal risks of mood disturbances.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Gingerol, a compound found in ginger, has been used in traditional medicine across Asia for centuries. It is noted for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits. Its cultural significance includes its use in traditional remedies and culinary practices. Proponents highlight its health benefits, while opponents may question its effectiveness compared to modern treatments. Its use spans both traditional and contemporary health practices.
 |
