|
Name: Ginsenosides
Type: Herbal supplement
AKA: Ginseng, Panax

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
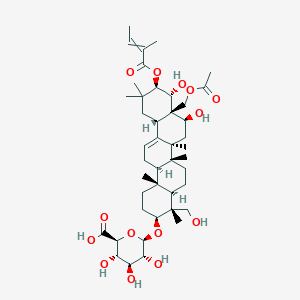
|
|
IV. History
Ginsenosides, the active compounds in ginseng, have been used in traditional medicine for thousands of years. They are studied for their potential health benefits, including adaptogenic and anti-inflammatory effects.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Ginsenosides are active compounds found in ginseng. They are not controlled substances and are legal globally. Regulations focus on their use in dietary supplements and herbal medicine, ensuring safety and efficacy. [Source: UNODC].
Key US Federal Policies:
Ginseng supplements are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements. They must meet standards for labeling, purity, and safety.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Ginsenosides are active compounds found in ginseng with potential adaptogenic properties. They are used to improve energy and cognitive function. Short-term use is generally safe, but excessive consumption may lead to side effects such as insomnia or gastrointestinal discomfort. Safe use involves adhering to recommended dosages. Recent research highlights their potential health benefits and mechanisms of action.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Ginsenosides do not have strong psychoactive effects but are believed to help improve mental clarity and reduce stress.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Ginsenosides, compounds found in ginseng, have been used in traditional Asian medicine for centuries. They are mentioned in ancient Chinese texts and are known for their purported health benefits. In modern culture, ginsenosides are popular in dietary supplements for their supposed cognitive and energy-boosting effects. Proponents value their traditional uses and health benefits, while opponents question the scientific evidence. Their use spans both traditional and contemporary health practices.
 |
