|
Name: Glutamine
Type: Amino Acid Supplement
AKA: L-Glutamine

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
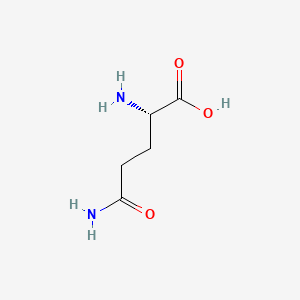
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Glutamine, an amino acid, has been used since the mid-20th century in various medical and sports applications. Its role in protein synthesis and immune function has been widely recognized. Glutamine's history includes its use in treating conditions like trauma and surgery recovery, reflecting its importance in nutritional and therapeutic contexts.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Glutamine, an amino acid, is legally available worldwide and widely used in dietary supplements and medical nutrition. It is not a controlled substance and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS). Regulatory agencies like the FDA monitor its safety, ensuring it meets health standards. Trends indicate ongoing acceptance and use in promoting muscle recovery and immune support.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Glutamine is an amino acid that supports various bodily functions, including muscle repair and immune system health. It does not act as a stimulant or depressant but may impact metabolic processes. Short-term use is generally safe, though excessive amounts may cause gastrointestinal issues. Safe doses range from 5-10 grams daily. Recent research underscores its benefits in recovery and metabolism with minimal adverse effects when used appropriately.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Glutamine, an amino acid, supports neurotransmitter synthesis and brain function. Immediate effects include improved cognitive function and mood stabilization. Long-term use is generally well-tolerated, with potential benefits for mood and cognition. Recent studies highlight its role in supporting brain health and mood regulation, with few adverse psychological effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Glutamine is an amino acid important for various bodily functions, including immune support and muscle recovery. It is widely used as a dietary supplement by athletes and individuals seeking to enhance physical performance and recovery. Historically, amino acids have been recognized for their essential roles in nutrition and health. Glutamine's cultural significance lies in its popularity within the fitness and wellness communities, reflecting broader trends in health supplementation and the pursuit of optimal physical condition. Media often discusses its benefits and the scientific evidence supporting its use, contributing to ongoing conversations about nutrition, exercise, and dietary supplements.
 |
