|
Name: Isobutyryl fentanyl
Type: Synthetic opioid
AKA: N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylisobutyramide

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
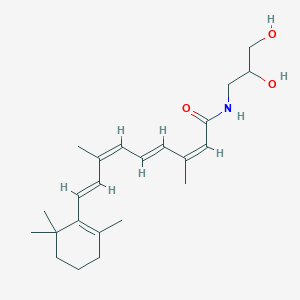
|
|
IV. History
Isobutyryl fentanyl, a fentanyl analog, was developed in the 21st century. It is known for its potent opioid effects and poses significant risks of overdose and abuse.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Isobutyryl Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid with high abuse potential. It is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States and similarly regulated globally to control its misuse and protect public health. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Isobutyryl fentanyl is a synthetic opioid with potent analgesic effects. It causes sedation, respiratory depression, and constricted pupils. Short-term use is effective for pain management, but long-term use can lead to addiction, tolerance, and severe health issues. Overdose risks include fatal respiratory depression. Safe use involves strict dosing and medical supervision. Recent research highlights its potency and risks compared to other opioids.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Isobutyryl fentanyl, a potent opioid, affects mu-opioid receptors, leading to strong euphoria and analgesia. Immediate effects include intense mood elevation and sedation, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in severe addiction, cognitive impairments, and mood disorders. Research emphasizes its potency and the associated risks of psychological dependence and cognitive effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Isobutyryl fentanyl is a synthetic opioid with no significant historical or cultural lore. It is part of the broader opioid crisis, with recreational use leading to significant health risks and societal issues. Its modern cultural impact is tied to the debates over synthetic opioids, their regulation, and their role in the opioid epidemic. Proponents of strict regulation emphasize the dangers of abuse and overdose, while some argue for its medical utility under controlled conditions. Its use is primarily illicit, contributing to public health and law enforcement challenges.
 |
