|
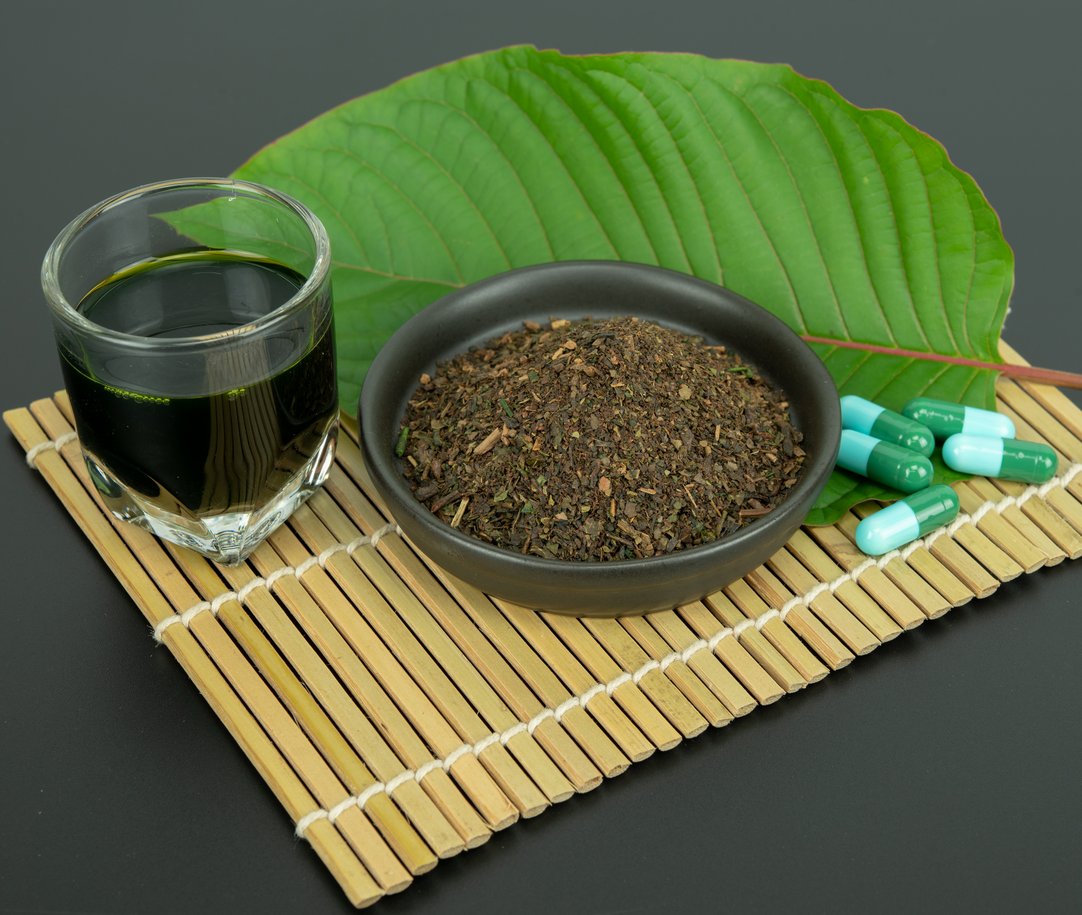
Name: Kratom
Type: Herbal
AKA: Mitragyna speciosa, biak-biak, ketum, kakuam

|
|
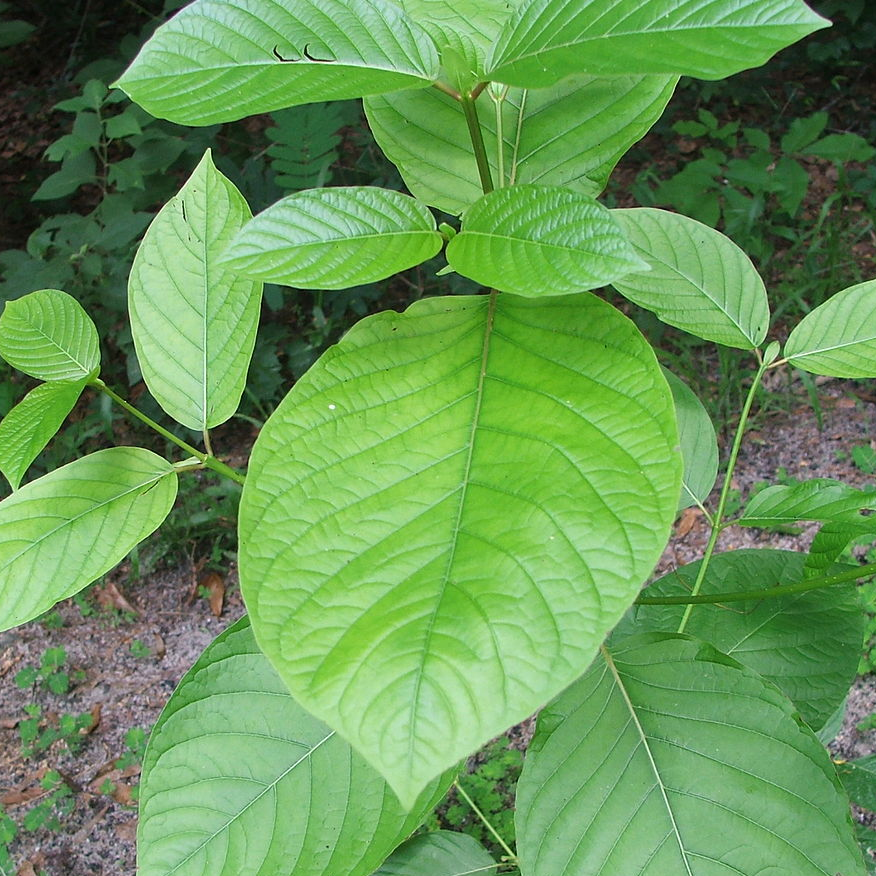
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
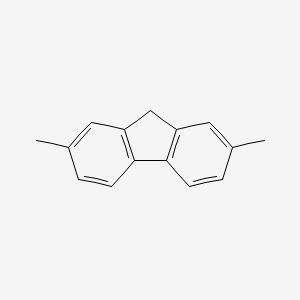
|
|
IV. History
Kratom, derived from the leaves of the Mitragyna speciosa tree, has been used in Southeast Asia for centuries for its stimulant and analgesic properties. It plays a significant role in traditional medicine and culture in countries like Thailand and Malaysia.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Kratom is a plant with stimulant and sedative effects. It is controlled differently across regions, with some areas allowing its use while others impose restrictions due to potential health risks. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Kratom, derived from a Southeast Asian tree, acts as both a stimulant and a sedative depending on the dose. At low doses, it increases energy and alertness, while high doses cause sedation and pain relief. Short-term effects include euphoria and increased sociability, while long-term use can lead to addiction, liver damage, and gastrointestinal issues. Overdose risks include respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use involves low doses and medical supervision. Recent research highlights its complex effects and potential for addiction.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Kratom, a tropical plant, provides mood enhancement, increased energy, and analgesia. Immediate effects include improved mood and cognitive stimulation. Long-term use can lead to dependence, tolerance, and potential mood swings. Chronic use is associated with cognitive impairments and mood disorders. Recent studies emphasize its complex psychological effects and risks of dependence.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Kratom is a plant used for its stimulant and sedative effects, classifying it as both an upper and a downer. Short-term use can increase energy and alleviate pain, while long-term use can lead to dependence, liver damage, and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include severe sedation, respiratory depression, and potential for psychosis. Safe dosages are typically up to 300 mg of alkaloids per day. Recent research emphasizes its potential for dependence and significant health risks. Physical effects include increased energy at low doses, drowsiness at high doses, and potential respiratory depression.
 |
