|
Name: Levothyroxine
Type: Thyroid hormone
AKA: Synthroid, Euthyrox, Levoxyl

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
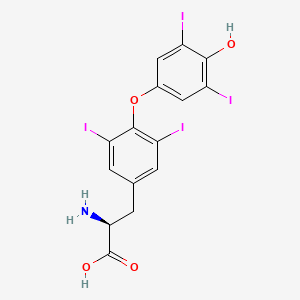
|
|
IV. History
Levothyroxine, a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine, has been in use since the 1950s. It is commonly prescribed for thyroid hormone replacement therapy in conditions like hypothyroidism. Its introduction revolutionized the treatment of thyroid disorders and remains a cornerstone of endocrine therapy.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Levothyroxine, a thyroid hormone replacement, is not classified as a controlled substance. It is regulated as a prescription medication due to its therapeutic use.
Key US Federal Policies:
Levothyroxine is regulated by the FDA, with specific guidelines for prescription use to ensure safety and efficacy.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Levothyroxine is a synthetic thyroid hormone used to treat hypothyroidism. As an upper, it supports normal thyroid function and metabolism. Short-term effects include improved energy levels and metabolic rate, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal risks. Overdose risks involve hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular issues. Safe dosing is typically guided by a healthcare provider. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and safety in managing thyroid conditions.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Levothyroxine, a thyroid hormone replacement, influences mood and cognition by normalizing thyroid hormone levels. Immediate effects include improved mood and cognitive function if thyroid levels are low. Long-term use helps maintain mental health stability. Research supports its role in alleviating symptoms of depression and cognitive decline associated with hypothyroidism.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Levothyroxine is a synthetic thyroid hormone used since the mid-20th century to treat hypothyroidism. It is mentioned in medical texts and has significant cultural impact due to its role in managing thyroid disorders. Proponents highlight its effectiveness in normalizing thyroid function, while opponents may discuss issues related to overuse or misuse. Its use is primarily medicinal, reflecting ongoing themes in endocrine health.
 |
