|
Name: Lorcaserin
Type: Serotonin receptor agonist
AKA: Belviq

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
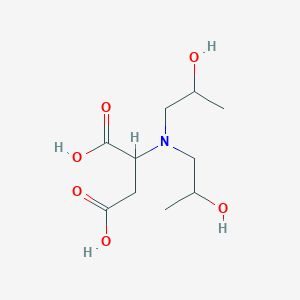
|
|
IV. History
Lorcaserin is a weight loss medication that was first approved by the FDA in 2012. It works by activating serotonin receptors in the brain to promote feelings of fullness and reduce appetite. Developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals, lorcaserin was marketed under the brand name Belviq. Despite its initial promise, lorcaserin was withdrawn from the market in 2020 due to concerns over an increased risk of cancer.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Lorcaserin was a Schedule IV controlled substance in the US due to its potential for abuse and dependence. It was used as a weight-loss medication but was withdrawn from the market in 2020 due to concerns about an increased risk of cancer. Globally, lorcaserin's legal status varied, with similar controls and regulatory concerns leading to its removal from many markets.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Lorcaserin, an anti-obesity medication, works as a serotonin receptor agonist to promote satiety. As an upper, it can affect mood and appetite regulation. Short-term effects include weight loss and improved satiety, while long-term use may lead to serotonin syndrome or heart valve issues. Overdose risks involve confusion and potential hallucinations. Safe dosage is typically 10-20 mg twice daily. Recent findings highlight its efficacy in weight management but also raise concerns about long-term cardiovascular risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Lorcaserin, a serotonin receptor agonist, impacts mood and appetite. Psychological effects include reduced anxiety and improved mood, though long-term use may lead to cognitive effects and mood disorders. Effects last 12-24 hours, with recent research examining its efficacy in treating obesity and potential psychological side effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Lorcaserin, an appetite suppressant, was developed in the early 21st century to combat obesity. Its cultural significance lies in the broader narrative of weight loss and the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to address rising obesity rates. The substance represents the modern medical approach to managing weight through pharmacological means. While it has not attained widespread cultural prominence, its role in the ongoing fight against obesity highlights the societal emphasis on health, body image, and the quest for effective weight management solutions. Debates over its safety and efficacy reflect the challenges of developing and regulating weight loss medications.
 |
