|
Name: Lysergic acid amide
Type: Hallucinogen
AKA: LSD precursor, LSD, acid, tabs, drops

|
|
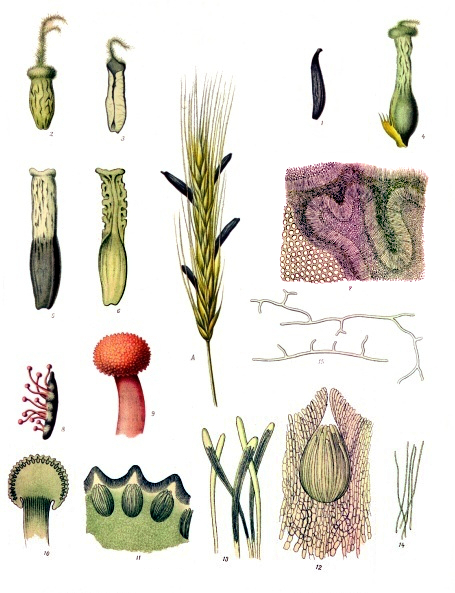
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Lysergic acid amide (LSA) is a naturally occurring compound found in certain plants like morning glories and Hawaiian baby woodrose. It has been used traditionally in various cultures for its psychoactive effects. LSA is chemically similar to LSD and can produce similar, albeit milder, effects. Its traditional use in spiritual and religious ceremonies highlights its cultural significance.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Lysergic acid amide (LSA) is a naturally occurring psychedelic that is generally not controlled in the US, though its legal status can vary by state. Globally, LSA is less regulated compared to LSD, but it can fall under analog laws in some jurisdictions. There is a trend towards increasing interest in psychedelic substances, but LSA remains largely unregulated with limited legal constraints.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Lysergic acid amide (LSA), a naturally occurring psychedelic, is known for its hallucinogenic properties. As an upper, it can cause altered sensory perception and mood changes. Short-term effects include visual distortions and altered reality, while long-term use may lead to persistent psychosis or perceptual disturbances. Overdose is rare but can cause severe anxiety and delirium. Safe use involves understanding individual tolerance, though regular use is generally discouraged. Recent research emphasizes its potential therapeutic uses and the need for further study.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Lysergic acid amide (LSA) affects serotonin receptors, causing altered perception and mood. Psychological effects are similar to LSD but generally less intense. Effects last 6-8 hours, with risks of anxiety and potential long-term changes in perception. Recent research examines its therapeutic potential and comparative effects with other psychedelics.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Lysergic acid amide (LSA), a naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in seeds of certain plants like morning glory and Hawaiian baby woodrose, has been used in traditional ceremonies by indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica for centuries. Its cultural significance is rooted in its role in spiritual and shamanic practices, similar to other psychedelics like psilocybin and mescaline. In modern culture, LSA is often overshadowed by its more famous relative, LSD, but it remains part of the broader psychedelic narrative. Its use in contemporary settings is typically recreational or for personal spiritual exploration, reflecting the enduring human interest in altered states of consciousness.
 |
