|
Name: Metformin
Type: Antidiabetic agent
AKA: Glucophage, Glumetza, Fortamet

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
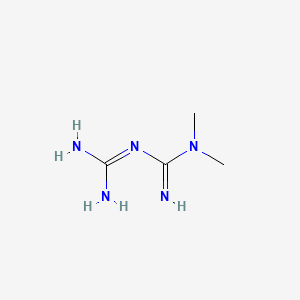
|
|
IV. History
Metformin, an antidiabetic medication, has been used since the 1950s. It is a cornerstone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, representing a significant advancement in diabetes management.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Metformin, a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, is widely available by prescription and is not classified as a controlled substance. It is approved for medical use in many countries. Regulatory bodies like the FDA ensure its safety and efficacy. The UNODC does not classify it as a major concern. Trends show its continued widespread use in diabetes management.
Key US Federal Policies:
Metformin is regulated by the FDA, with specific guidelines for prescription use to ensure safety and efficacy.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Metformin is a medication used to manage type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity. It acts as an upper in terms of energy levels and metabolic function. Short-term use is effective for managing blood glucose levels, while long-term use is generally safe but may cause gastrointestinal issues and, rarely, lactic acidosis. Safe use involves regular monitoring of blood glucose and renal function. Recent research highlights its efficacy in diabetes management and potential benefits for longevity.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Metformin, primarily a diabetes medication, has minimal direct psychological effects. Immediate effects include potential improvements in mood due to better glycemic control. Long-term use may contribute to overall well-being and minor psychological benefits. Research focuses on its primary role in managing blood glucose levels and indirect effects on mood through metabolic improvements.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Metformin, a widely used medication for type 2 diabetes, has no significant cultural lore but is well-documented in modern medical literature. It has been used since the mid-20th century and is a staple in diabetes management globally. Its cultural significance lies in its impact on public health, with millions of people benefiting from its use. Proponents include medical professionals and patients, while there are no significant opponents. Its use is strictly medicinal, with a well-established safety profile and significant positive impact on diabetes management.
 |
