|
Name: Methadone
Type: Opioid
AKA: Dolophine, Methadose, Amidone
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
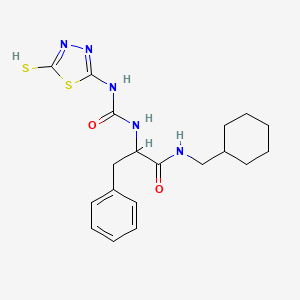
|
|
IV. History
Methadone, a synthetic opioid, was developed in the 1940s as a pain reliever and later as a treatment for opioid addiction. It has been used in managing chronic pain and as part of opioid replacement therapy, contributing to addiction treatment strategies.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Methadone is a synthetic opioid used for pain management and as a treatment for opioid addiction. It is a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States, where it is classified as Schedule II. Methadone's use is regulated to prevent abuse, with strict laws governing its prescription and distribution. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Methadone is a synthetic opioid used for pain relief and as part of drug addiction detox programs. It causes sedation, respiratory depression, and constricted pupils. Short-term use is effective for pain management and opioid withdrawal, but long-term use poses risks of dependence and overdose. Overdose risks include fatal respiratory depression. Safe use involves careful dosing and medical supervision. Recent research emphasizes its effectiveness in managing pain and opioid addiction, and its potential for overdose.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Methadone, an opioid used for pain relief and addiction treatment, affects mu-opioid receptors, providing analgesia and mood enhancement. Immediate effects include euphoria and sedation, lasting several hours. Long-term use can lead to dependence, cognitive impairments, and mood disturbances. Recent studies focus on its efficacy in addiction treatment and risks of cognitive and mood changes with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Methadone is an opioid used in pain management and as a part of drug addiction detoxification. Its cultural significance lies in its role in treating opioid addiction and managing pain. Media coverage often discusses its effectiveness in addiction treatment and the risks associated with long-term use. Methadone is used medicinally and is part of broader discussions about drug policy and addiction treatment.
 |
