|
Name: Methcathinone
Type: Stimulant
AKA: N-Methylcathinone, "cat"

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
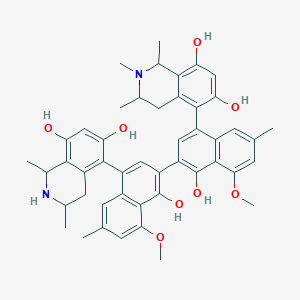
|
|
IV. History
Methcathinone, a synthetic stimulant, was first synthesized in the 1920s. It gained prominence in the 2000s as a recreational drug due to its stimulant effects. Its development reflects the broader history of synthetic stimulants and their impact on drug culture and regulation.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Methcathinone is a synthetic stimulant similar to methamphetamine, known for its high potential for abuse. Globally, it is often regulated under analog acts due to its stimulant effects. In the U.S., it is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance, reflecting its lack of accepted medical use and high abuse potential. Many countries have implemented strict controls, following trends in increasing regulation to combat its misuse. The UNODC also monitors its status and distribution. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Methcathinone is a synthetic stimulant similar to methamphetamine. It acts as an upper, increasing energy and alertness. Short-term use can lead to euphoria and heightened physical performance, but long-term use poses risks of cardiovascular issues and psychological effects. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular effects. Safe use requires cautious dosing. Recent research explores its stimulant effects and health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Methcathinone, a stimulant, affects monoamine systems, leading to increased alertness and euphoria. Immediate effects include enhanced mood and cognitive stimulation, with effects lasting several hours. Long-term use can cause dependence and psychological issues such as anxiety and cognitive decline. Recent research highlights risks of severe mental health disturbances with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Methcathinone, a synthetic stimulant, gained attention in the late 20th century. It is known for its stimulant and empathogenic effects, with cultural significance tied to its role in recreational drug use. Proponents discuss its stimulant properties, while opponents focus on its potential for abuse and health risks. Its use is primarily recreational, with concerns about its safety and legal status.
 |
