|
Name: Methylphenidate
Type: Stimulant
AKA: Concerta, Ritalin, Methylin

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
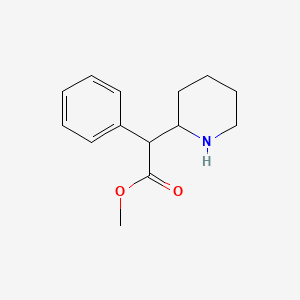
|
|
IV. History
Methylphenidate was first synthesized in the 1950s and introduced as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It was initially marketed under the name Ritalin. Its stimulant properties and effectiveness in managing ADHD symptoms have made it widely used, with significant growth in its prescription for children and adults. Methylphenidate's role in managing ADHD has become a key aspect of its use in both clinical and educational settings.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Methylphenidate is a stimulant used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. It is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance in the U.S. due to its potential for abuse. Globally, its regulation is similarly strict, with trends towards increasing control to prevent misuse and manage addiction. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Methylphenidate is a stimulant used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. It increases focus, attention, and energy. Short-term effects include improved cognitive performance and alertness, while long-term use may lead to dependence and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular problems. Safe dosing is essential, and recent research focuses on its efficacy in ADHD treatment and potential for abuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Methylphenidate is a stimulant used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. Immediate effects include improved focus, mood elevation, and increased alertness. Long-term use can lead to dependence, anxiety, and potential cognitive impairment. Chronic use is associated with mood swings and potential development of psychiatric disorders. Recent research highlights the benefits and risks in treating ADHD.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Methylphenidate, known for treating ADHD, was first synthesized in the 1950s. It has been used extensively in educational and medical settings to manage attention deficit disorders. Its cultural impact includes debates about its use in both children and adults, with discussions about its effectiveness versus potential misuse. Proponents argue for its benefits in managing ADHD symptoms, while opponents raise concerns about overprescription and its impact on education.
 |
