|
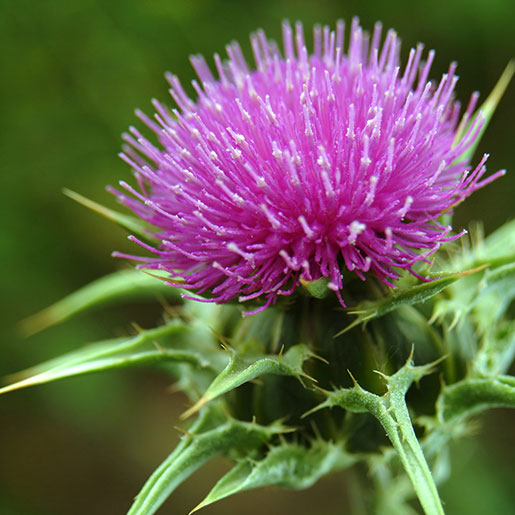
Name: Milk Thistle
Type: Medicinal Herb
AKA: Silybum marianum

|
|
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
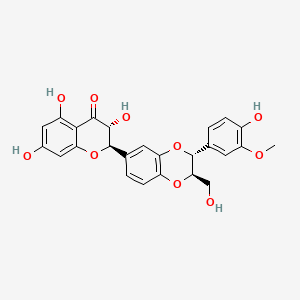
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
Milk Thistle is a plant, not a single chemical compound. Its main active component is silymarin, a mixture of flavonolignans. The IUPAC name for silybin, a major constituent of silymarin, is:
2-[(2R,3R)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl]-2,3-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
|
|
IV. History
Milk thistle, derived from Silybum marianum, has been used in traditional medicine for over 2,000 years. It is known for its liver-protective properties and has been used to treat liver diseases and detoxification. It is commonly used in herbal supplements and continues to be valued for its potential health benefits.

|
|
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Milk thistle is a herbal supplement known for its liver-protective properties. It may cause mild gastrointestinal effects. Short-term use supports liver health, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal side effects. Overdose risks are low, but excessive use may cause digestive issues. Safe use involves adherence to recommended doses. Recent research highlights its benefits for liver health and potential interactions with other medications.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Milk thistle, used for liver health, has minimal direct psychological effects. Immediate benefits include potential mood improvement due to overall health benefits. Long-term use supports physical health, which can indirectly benefit mental well-being. Recent studies suggest minimal direct psychological impact, with benefits mainly related to physical health rather than direct mental effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Milk thistle has been used since ancient times for its liver-protective properties. It is mentioned in historical texts from various cultures, including Greco-Roman medicine. In modern times, it is popular in herbal medicine for liver health. Proponents highlight its benefits, while opponents question its efficacy and scientific support. Its use spans both traditional medicine and contemporary health practices.
 |
