|
Name: Moramide-intermediate
Type: Opioid
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
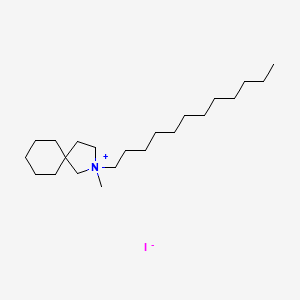
|
|
IV. History
Moramide, developed in the 1950s, is an opioid analgesic used for pain management. Its development marked a significant advancement in opioid medications, though its use has been limited by its addictive properties.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Moramide Intermediate, a precursor in the synthesis of narcotic analgesics, is regulated as a controlled substance due to its potential for misuse. Its status reflects regulations aimed at preventing abuse.
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Moramide Intermediate is a substance used in the synthesis of other drugs. As a downer, it has sedative properties. Short-term effects include relaxation and reduced anxiety, while long-term use may have limited research. Overdose risks involve excessive sedation and potential respiratory issues. Safe use requires careful handling, and recent research emphasizes its role in drug synthesis.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Moramide intermediate, an opioid, affects opioid receptors, leading to euphoria and cognitive impairment. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and pain relief, while long-term use can lead to dependence and psychological issues such as depression. Effects last several hours, with chronic use linked to severe mental health issues and cognitive decline.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Moramide Intermediate is a chemical precursor in the synthesis of opioids, with no historical or cultural lore. Its significance is primarily industrial, related to pharmaceutical manufacturing. Discussions focus on its role in opioid production and the associated risks of misuse and diversion. Its use is strictly industrial and medicinal, reflecting broader issues in opioid production and regulation.
 |
