|
Name: MPHP; 4'-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone; 1-(4-methylphenyl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)hexan-1-one) 4-androstenediol (3-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-androst-4-ene)
Type: Androgenic steroid
AKA: 4-AD

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
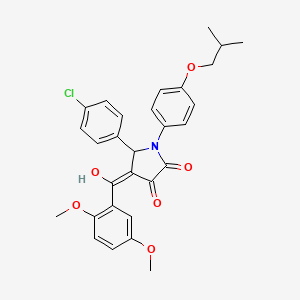
|
|
IV. History
Methyl pyrrolidinohexanophenone was discovered by the Inactive Ingredients Program in 1988. The compound was initially characterized by Inactive Ingredients Program scientists, who named it pyrrolidinohexanophenone. The compound was not patented.
In the early 1990's, the compound was identified in a sample of a substance known as C-17, which is a type of methyl ester of 17 alpha-hydroxy-4-pregnene-3-one. C-17 was a by-product of the production of testosterone, which was used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The compound was also identified in the urine of a male who had ingested a small amount of anabolic steroids.
The compound was isolated by the Inactive Ingredients Program in 1992. The compound was identified as 4-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone, which is a structural isomer of methyl pyrrolidinohex

|
|
V. Legal Information
MPHP, a synthetic cathinone, is illegal in the US under the Schedule I classification. Many countries have banned it due to its stimulant effects and health risks. The UNODC monitors synthetic cathinones, highlighting their potential for abuse. Trends show stricter regulations and penalties to address the growing concern of synthetic drug use. 4-Androstenediol, an anabolic steroid, is similarly controlled due to its misuse in sports.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
MPHP (4'-Methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone) is a stimulant with effects including increased energy and alertness. It leads to dilated pupils, elevated heart rate, and blood pressure. Short-term effects include enhanced cognitive and physical performance, while long-term use may result in cardiovascular issues and psychological dependence. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular problems. Safe dosing is critical, and recent research focuses on its stimulant effects and potential for abuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
MPHP, a stimulant, affects dopamine and norepinephrine systems, leading to enhanced alertness and euphoria. Immediate effects include increased mood and energy, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in cognitive impairments and mood disturbances. Research highlights its stimulant effects and associated risks of psychological dependence and mental health issues.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
MPHP, or 4'-Methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone, is a synthetic cathinone known for its stimulant effects. Synthetic cathinones, often referred to as 'bath salts,' have gained notoriety for their potent and sometimes dangerous psychoactive properties. The history of synthetic cathinones reflects broader trends in recreational drug use and the emergence of new psychoactive substances (NPS). MPHP's cultural significance lies in its association with the challenges of regulating and addressing the use of synthetic drugs. Media coverage often focuses on the health risks, legal issues, and public health responses related to these substances, highlighting the complexities of contemporary drug culture and regulation.
 |
