|
Name: Nabilone
Type: Cannabinoid receptor agonist
AKA: Cesamet
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
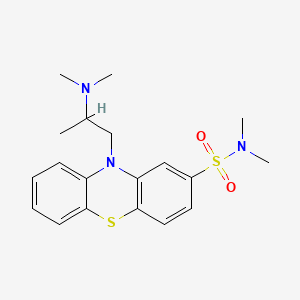
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Nabilone is a synthetic cannabinoid similar to THC, the active component of cannabis. It was approved by the FDA in 1985 for the treatment of nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. Nabilone is also used for pain management in certain conditions. Its approval marked an important step in recognizing the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Nabilone, a synthetic cannabinoid used for treating nausea, is a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. In the US, it is classified as a Schedule II drug. Globally, nabilone is regulated with a focus on its therapeutic use in managing chemotherapy-induced nausea, while efforts are made to prevent misuse.
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Nabilone is a synthetic cannabinoid used for nausea and appetite stimulation. It acts as an upper, causing euphoria and appetite enhancement. Short-term use is effective for managing chemotherapy-induced nausea, but long-term use may have cognitive and psychological effects. Safe use involves medical supervision and careful dosing. Recent research supports its efficacy in nausea management and explores its broader therapeutic potential.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Nabilone, a synthetic cannabinoid, interacts with cannabinoid receptors to alleviate nausea and improve mood. Immediate effects include euphoria and relaxation, while long-term use may have cognitive implications. Research focuses on its efficacy for nausea and its overall impact on mental health.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Nabilone is a synthetic cannabinoid used primarily as an antiemetic and appetite stimulant. Its cultural significance is tied to its role in medical cannabis, providing relief for nausea and stimulating appetite in patients undergoing chemotherapy or suffering from anorexia. Nabilone reflects the growing acceptance and integration of cannabinoid-based therapies in mainstream medicine. Its role in the cultural narrative is one of bridging traditional cannabis use with modern medical applications, contributing to the broader discussion of cannabinoids in healthcare.
 |
