|
Name: Normethadone
Type: Opioid
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
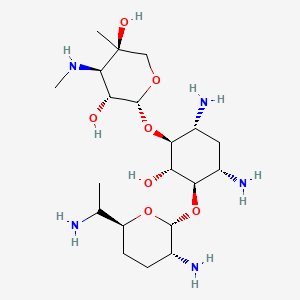
|
|
IV. History
Normethadone is a synthetic opioid developed in the mid-20th century. It was used primarily for its analgesic properties. Normethadone is a metabolite of methadone, a more widely used opioid. While not commonly used in modern medical practice, normethadone contributed to the understanding of opioid metabolism and the development of methadone maintenance therapy.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Normethadone is a metabolite of methadone, a controlled substance used in opioid addiction treatment. While normethadone itself is not widely regulated, methadone is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance in the US. The legal status of normethadone is less defined, but it may be subject to regulations that govern its parent compound. Globally, the trend is towards controlling opioids and their metabolites to address abuse and addiction concerns.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Normethadone, a metabolite of methadone, is used in pain management. As a downer, it provides analgesia and sedation. Short-term effects include pain relief and drowsiness, while long-term use can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Overdose risks include respiratory depression and potentially fatal outcomes. Safe dosing should be closely monitored, with typical use at low doses. Recent findings emphasize the risks of opioid metabolites and the importance of regulating their use to avoid addiction and overdose.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Normethadone, a methadone analog, affects opioid receptors, leading to pain relief and mood alteration. Psychological effects include potential euphoria and sedation. Long-term use can result in dependence and cognitive impairments. Recent research explores its effects compared to other opioids and its potential for abuse.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Normethadone, an opioid analgesic, has been used since the mid-20th century primarily in medical settings. Its cultural significance is relatively minor compared to more widely known opioids. However, it represents the continuous search for effective pain management solutions within the medical community. The substance is part of the larger narrative surrounding opioid use, addiction, and regulation. Normethadone underscores the complexities of opioid pharmacotherapy and the ongoing efforts to balance therapeutic benefits with the risks of dependency and misuse.
 |
