|
Name: Normorphine
Type: Opioid
AKA: N/A

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
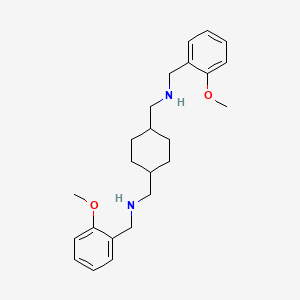
|
|
IV. History
Normorphine is a metabolite of morphine, one of the most widely used opioid analgesics. It is formed in the body through the demethylation of morphine. While normorphine itself is not used therapeutically, its identification is important in the context of pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism studies. The detection of normorphine in biological samples helps in understanding the metabolism and elimination of morphine.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Normorphine, a metabolite of morphine, is not typically listed as a controlled substance itself but is subject to regulation under general opioid laws. In the US, morphine is a Schedule II drug, and similar controls may apply to its metabolites. Globally, normorphine's legal status is influenced by the trend towards regulating opioids and their metabolites to address addiction and misuse concerns.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Normorphine, an opioid metabolite, provides analgesia and sedation. As a downer, it can cause reduced heart rate and respiratory depression. Short-term effects include pain relief, while long-term use may lead to addiction and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks include life-threatening respiratory depression. Safe use involves managing doses carefully. Recent findings emphasize its analgesic properties but also its potential for misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Normorphine, an opioid metabolite, affects opioid receptors, leading to euphoria and pain relief. Psychological effects include mood swings and potential cognitive impairment with long-term use. Research is limited but focuses on its metabolic pathways and impact on mental health.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Normorphine, an opioid metabolite, has been known since the early 20th century. Its cultural significance is minor compared to other opioids, but it represents the historical and ongoing use of morphine and its derivatives in pain management. Normorphine’s role in the opioid narrative underscores the continuous efforts to understand and improve opioid pharmacotherapy. The substance highlights the balance between therapeutic benefits and the risks of abuse and dependency. While it lacks the dramatic cultural impact of more prominent opioids, normorphine is part of the broader discourse on pain management and the challenges of opioid use in medicine.
 |
